Overview
When using Bizagi Web service connector to configure integration with external systems, you may go to the properties of each configured interface in order to use advanced settings.
Interfaces created through the interfaces wizard, either in the sixth step of the Process Wizard (Define Interfaces) or as an On Exit Task Event, are also viewed in this Systems module. Interfaces created through the interfaces wizard are immediately created under an auto-generated system called Default.
To locate these set interfaces, go to the Expert view and click the External Systems module.
Creating interfaces
To create a new interface from this view, make sure you have a created System with its Enable interfaces property active:
Then, right-click Interfaces of your created System, and click at the New interface option:
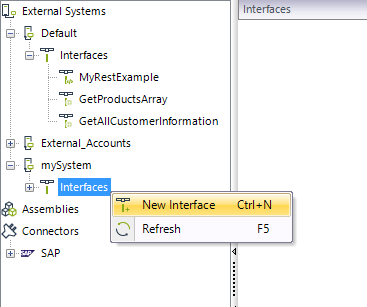
The following window will display:
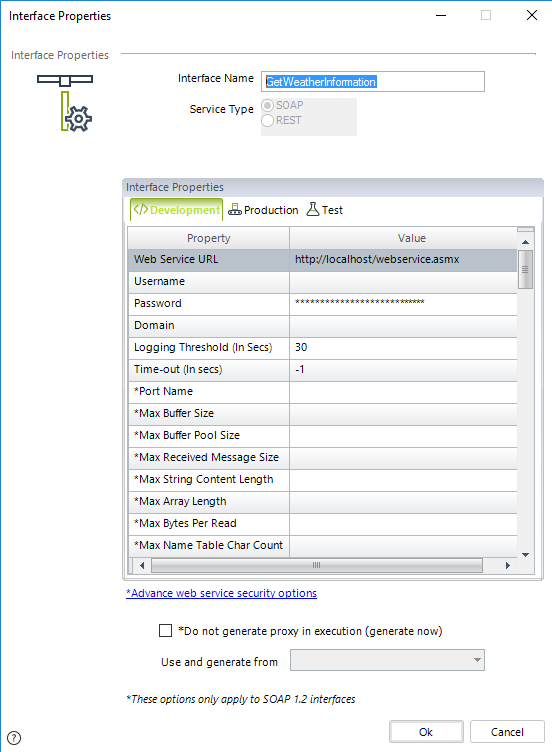
Notice that by default, the new interface will be treated as a SOAP web service interface (Service Type = SOAP).
The following fields are presented:
•Interface Name: The unique name for this interface which must not contain blank spaces (mandatory).
•Service Type: Possible values are SOAP or REST. When choosing REST as the service type, there will be no field to specify the service's method.
•Interface properties table: A set of values for configuration oriented towards the project's environments (Development, Test or Production). This set include:
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Web service URL |
The URL to access the service. For REST services, this will be the Base URL. |
Username |
When the service requires HTTP basic authentication, this username is required for the service access. |
Password |
When the service requires HTTP basic authentication, this password is required for the service access. |
Domain |
When the service requires HTTP basic authentication, this domain is optional to complement the username, for the service access. |
Logging Threshold (In Secs) |
The time in seconds which defines an expected service threshold for the interface. If the invocation exceeds this definition in execution, then it records a trace line in the .csv log recorded at the .\Temporary\SOA\Log\ path of your project (by default, one file per web service, as C:\Bizagi\Projects\[your_project]\Temporary\SOA\Log\[your_interface]Log_1.csv). This is especially helpful for monitoring purposes since each invocation having exceeded or having produced a timeout will record detail of: DateTime, ErrorDescription, idCase, Task_Name, URL, Method_Name, and InterfaceTime(MM:ss:mmm).
The default value is set to 30 seconds, so that it will always record execution detail when an invocation exceeds this time. |
Time-out (In Secs) |
The time in seconds which defines when to time out any attempt to invoke the interface. If the invocation exceeds this definition in execution, then the invocation throws an error and it is recorded in a trace line in the .csv log at the .\Temporary\SOA\Log\ path of your project (by default, one file per web service, as C:\Bizagi\Projects\[your_project]\Temporary\SOA\Log\[your_interface]Log_1.csv). This is especially helpful for monitoring purposes since each invocation having exceeded or having produced a timeout will record detail of: DateTime, ErrorDescription, idCase, Task_Name, URL, Method_Name, and InterfaceTime(MM:ss:mmm).
By default, its value is -1 which means that interfaces do not have an initial definition of when to timeout. The invocation will timeout according to this setting or the one defined for the activity if the invocation is done from an asynchronous activity (whichever has the lowest timeout definition). |
Port Name |
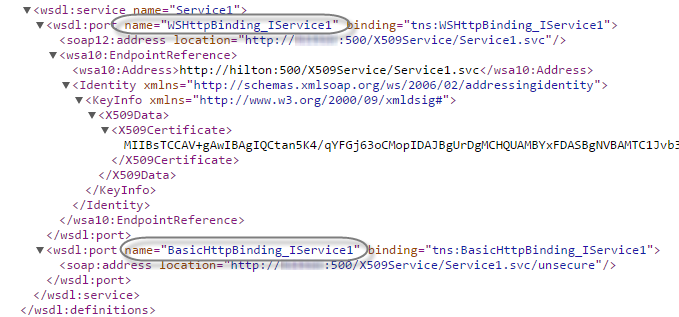
This field allows the user to write down a specific port name when there is the need to execute a SOAP web service that offers different service ports (i.e. SOAP 1.1, SOAP 2.0, etc.). Note that this port name can be configured separately according to each environment (i.e Development, Test, Production).
To specify the port name, consider entering it exactly as specified at the end of the service's WSDL definition:
|
Max Buffer Size |
Edit its value (increment it) in case you need to send a lot of information to your Web service (i.e a large file) that would normally exceed the default limit of sent information. Corresponds to the attribute maxBufferSize of the bindings element of the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) configuration File. Sets the maximum size of the SOAP headers. |
Max Buffer Pool Size |
Edit its value (increment it) in case you need to send a lot of information to your Web service (i.e a large file) that would normally exceed the default limit of sent information. Corresponds to the attribute maxBufferPoolSize of the bindings element of the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) configuration File. Sets the maximum amount of memory (in bytes) allocated. |
Max String Content Length |
Edit its value (increment it) in case you need to send a lot of information to your Web service (i.e a large file) that would normally exceed the default limit of sent information. Corresponds to the attribute maxStringContentLength of the readerQuotas element of the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) configuration File. Sets the maximum string length of the response. |
Max Array Length |
Edit its value (increment it) in case you need to send a lot of information to your Web service (i.e a large file) that would normally exceed the default limit of sent information. Corresponds to the attribute maxArrayLength of the readerQuotas element of the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) configuration File. Sets the maximum allowed array length. |
Max Bytes Per Read |
Edit its value (increment it) in case you need to send a lot of information to your Web service (i.e a large file) that would normally exceed the default limit of sent information. Corresponds to the attribute maxBytesPerRead of the readerQuotas element of the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) configuration File. Sets the maximum allowed bytes returned for each read. |
Max Name Table Char count |
Edit its value (increment it) in case you need to send a lot of information to your Web service (i.e a large file) that would normally exceed the default limit of sent information. Corresponds to the attribute maxNameTableCharCout of the readerQuotas element of the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) configuration File. Sets the maximum characters allowed in a table name. |
|
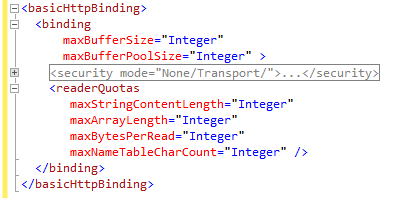
The values and data types of the attributes of Microsoft's Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) as explained above (parameters such as: max buffer size, max buffer pool size, max string content length, max array length, max bytes per read, and max name table char count), will end up set in the XML configuration file as shown below:
This will be the structure that Bizagi builds for the Web Service invocation. |
•Advanced web service security options:
Click on this link to configure the type of security used to authenticate and invoke your web service.
Include the security definition by using the Add button, selecting the type of security and inputting the credentials/tokens to authenticate.
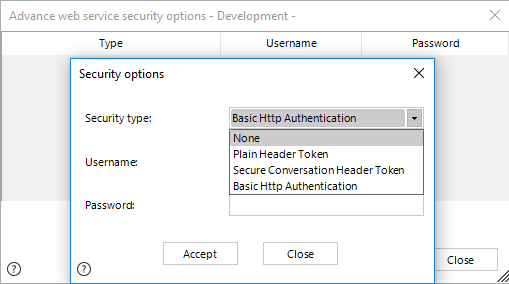
Notice this definition differs from the basic authentication credentials specified in the above properties (username, password, domain) mainly because the above definition is used for Bizagi to access the WSDL and physical resources used by the web service definition, while the definition in this configuration will determine the security involved in runtime at the web service itself.
Possible definitions supported by Bizagi, which you may include for the security of your interface are:
Option |
Description |
Specification |
|---|---|---|
Plain Header Token |
Sends out the user's token (usernameToken) within the SOAP header message, according to the WS-Security standard. |
According to the technical definition at: https://www.oasis-open.org/committees/download.php/16782/wss-v1.1-spec-os-UsernameTokenProfile.pdf |
Secure Conversation Header Token |
Sends the user's token according to the specification, having a valid certificate installed in client server. |
According to the technical definition at: http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-sx/ws-secureconversation/200512 |
Basic HTTP Authentication |
Sends out the credentials which apply when the service's end-point is protected (at a basic authentication level).
By default, Bizagi will attempt to use Basic HTTP Authentication if no security definition is specified, and if you are relying on basic authentication to protect the service's resources (by using the set credentials at the other properties, having username, domain and password). |
According to the technical definition at: |
•Do not generate proxy in execution (generate now):
Bizagi generates a proxy definition (a .cs and .dll file) for any external Web services that are integrated in the processes.
By default, this will be done the very first time that the service is looked upon and invoked in execution.
By generating a proxy from design time (in Bizagi Studio), you choose to use this definition on execution instead of generating a newer one.
This option is really useful when the setup of your Web services in a production environment have major security restrictions (its definition resources such as the WSDL or related schemas are not easily accessed).
With this option, you may generate the proxy from the WSDL configured in another environment (e.g, the development environment).
To do so, rely on the Use and generate from field to select the environment where the proxy will be generated.
|
For this feature to work, you will need to make sure that the WSDL involved to generate the proxy is exactly the same one used in the execution. |
Editing an existing interface
Once an interface has been defined and already configured in a Process, it is also possible to edit its information. Similarly as in the interface creation, the option to edit will mainly allow to: edit or include authentication credentials (for HTTP basic authentication), or to manage the Service's URL.
To edit an existing interface, right-click at the given interface and click its Properties option:
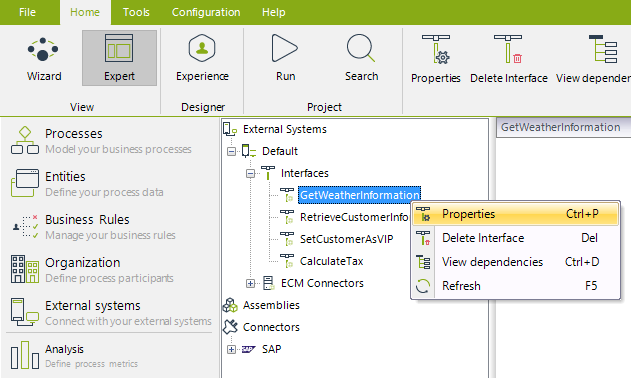
You will be able to specify or edit the properties described in the above section.
|
Editing REST services URL has certain considerations for its Base URL management. Click for more information about the considerations in REST services interfaces. |
Deleting an interface
To delete an interface, right-click the given interface and select the Delete interface option.
Bizagi will run its dependencies engine as a validation to make sure the interface is not currently being used in a Process version. Notice that you may not delete Interfaces that are already functional in the Production environment.
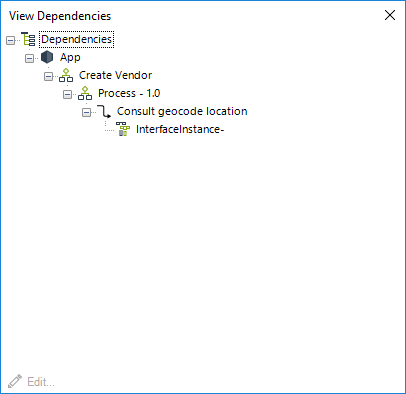
Interfaces in Production
The interfaces listed in this view in Bizagi Studio, will allow its information to be initially set for the different environments of your project (Development, Test or Production).
Once these interfaces have been deployed to Production, its management will be done directly in each separate environment as described in the System administration chapter, directly with the Management Console.
Last Updated 1/24/2025 4:50:45 PM