Tasks duration is used to calculate performance indicators and the status of pending activities in the Work Portal.
Duration can be static, defined in the Process Model or it can be dynamic, evaluated by an expression when the Task is created.
IMPORTANT
•Dynamic duration has to be defined in minutes or it must return a fixed date.
•Durations MUST be set On Enter of Activities to be taken into consideration. If the duration is not set On Enter, then Bizagi will use the static duration defined in the Process Model.
•Set Task duration - defining duration in time
•Set Task duration - with a fixed date
•Set duration of Timers attached to activities
•Set Timer duration considering the Working time schema and timezone of a user
Set Task duration - defining duration in time
Suppose you have a Travel Request process where the Administrative Department of your company locates and registers the travel bookings on your behalf. You can request a national or an international trip, and based on this locality, the booking administrator will have two or three days respectively to book the hotel and flight.
Since the duration of the task is not static we need an expression to set it.
National and international destinations are stored in a Parameter Entity, and are distinguished by a Code: "1" for national and "2" for international.
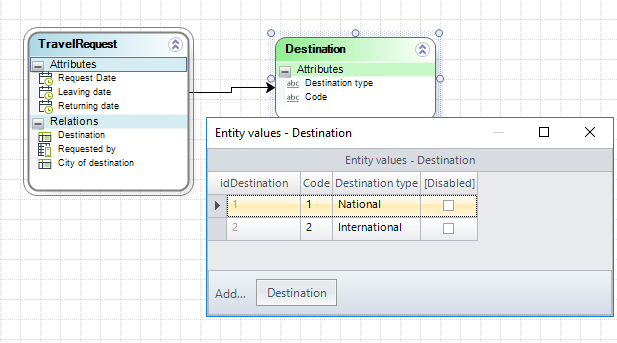
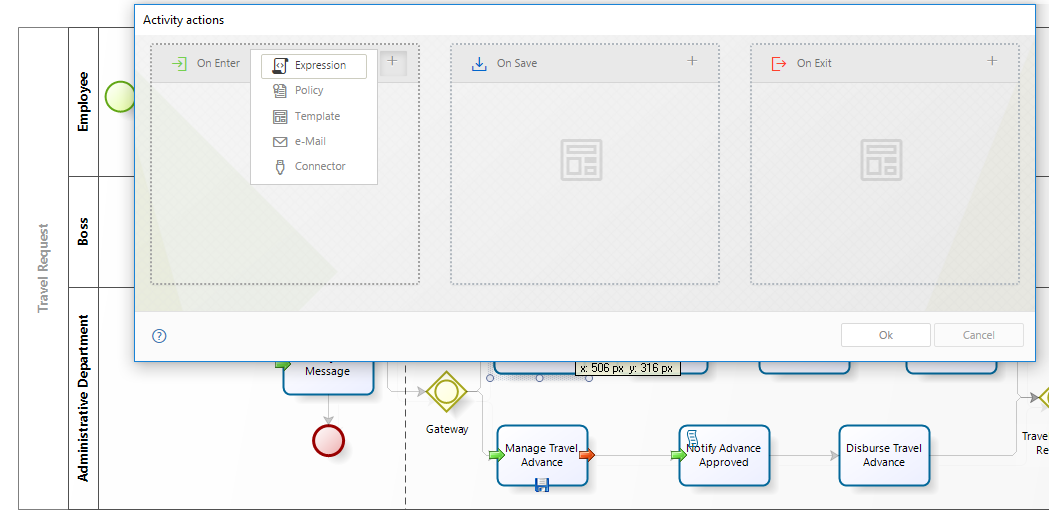
1. In the fourth step of the Bizagi Process Wizard (Business Rules), select Activity Actions.
Click the Task in which the duration will be calculated and create an On Enter Expression.
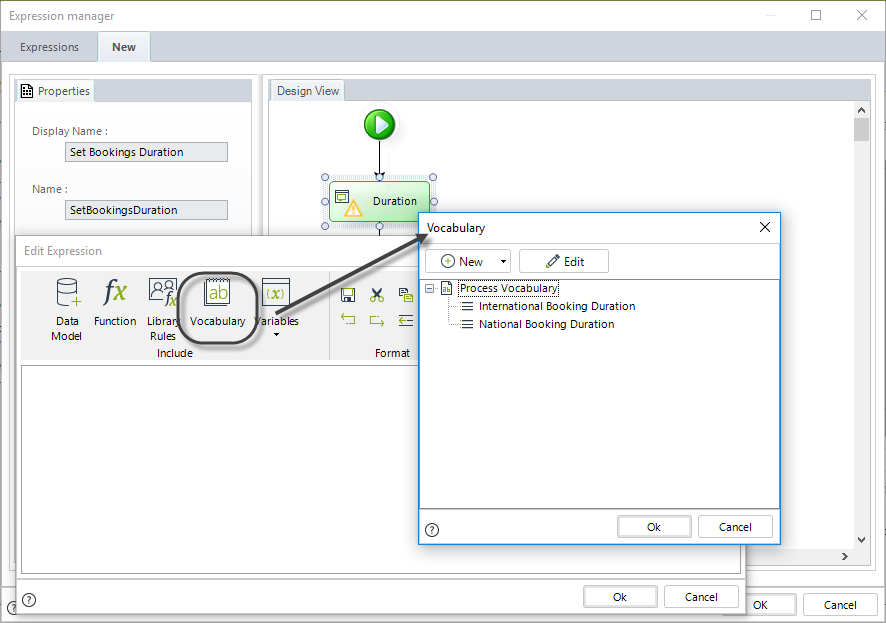
2. Create the expression to set the duration.
We recommend to use vocabularies to store constant duration for Tasks, to allow for easy modification in the Work Portal if the business condition should change.
In order to use vocabularies, they have to be created prior to the creation of the referencing expression.
We will use two previously defined constant vocabularies. These can be modified at any time by end users in the Work Portal, to respond to changing business needs.
3. Determine if the request is national or international.
Set the duration to the element in the vocabulary. This is done by using the Task Duration function available in the Function list of the Date & Time category.
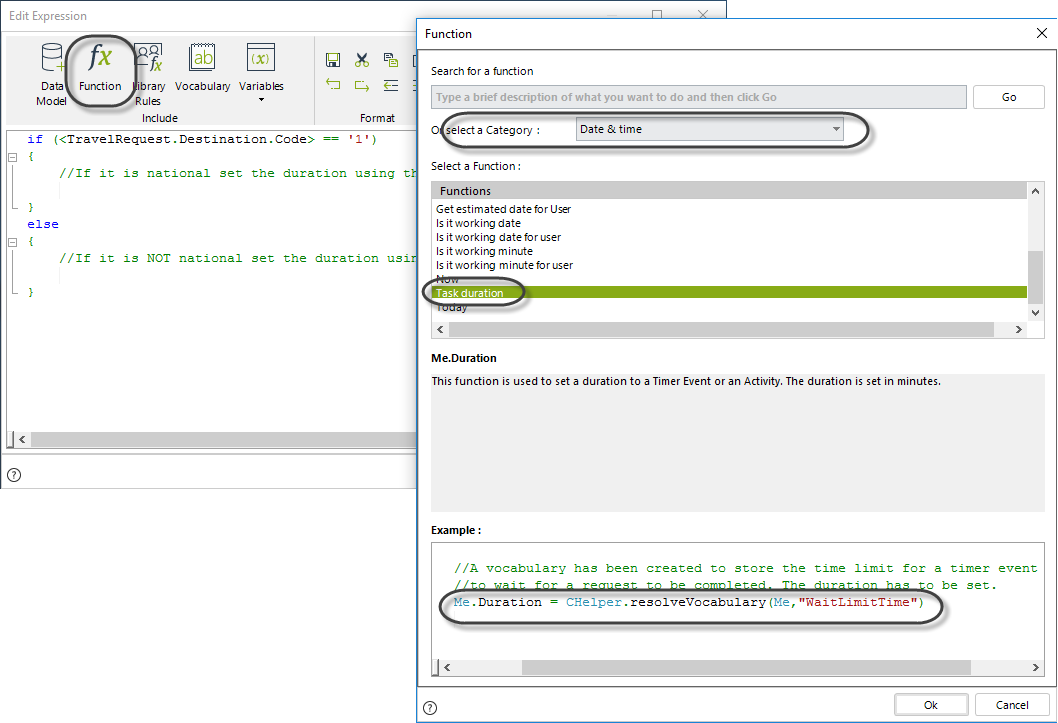
The next image shows the code of the expression:
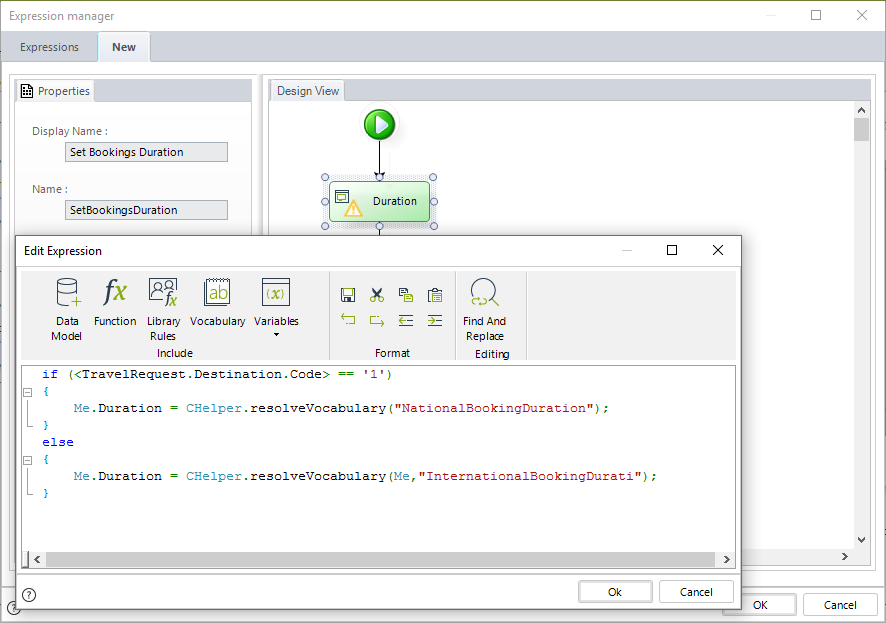
//Identify if the destination is national
if (<TravelRequest.Destination.Code> == '1')
{
//If it is national set the duration using the National vocabulary
Me.Duration = CHelper.resolveVocabulary("NationalBookingDuration");
}
else
{
//If it is NOT national set the duration using the international vocabulary
Me.Duration = CHelper.resolveVocabulary("InternationalBookingDurati");
}
Set Task duration - defining duration with a fixed date
Suppose you have a Travel Request process where the Administrative Department of your company locates and registers the travel bookings on your behalf. Based on the locality type of a request (i.e., a national or an international trip), the booking administrator will have up to one day before departure (Leaving Date) to book the hotel and flight.
1. In the fourth step of the Bizagi Process Wizard (Business Rules), select Activity Actions.
Click the Task in which the duration will be calculated and create an On Enter Expression.

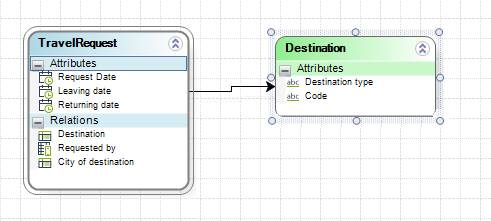
2. Declare the necessary variables.
In this example we need two variables of the date time type:
•LeavingDate: Stores the value of the Leaving Date attribute
•FixedDate: Stores the derived due date and will be used to set the Task Duration
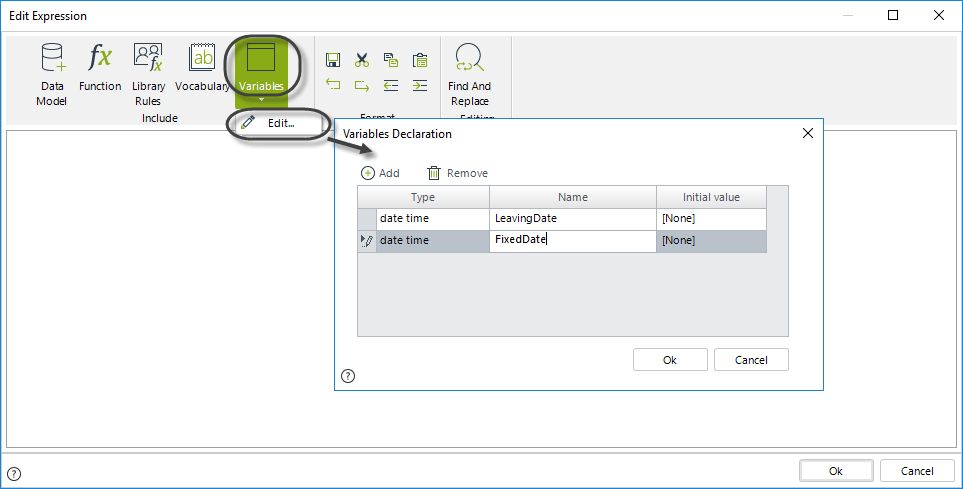
3. Create the expression to set the duration.
First retrieve the leaving date from the attribute Leaving Date by navigating the Data Model. The value will be set to the variable declared previously.
The Task duration will be set to one day prior to the LeavingDate.
To calculate this fixed date we subtract one day from the date stored in the LeavingDate variable.
The result is then assigned to the FixedDate variable.
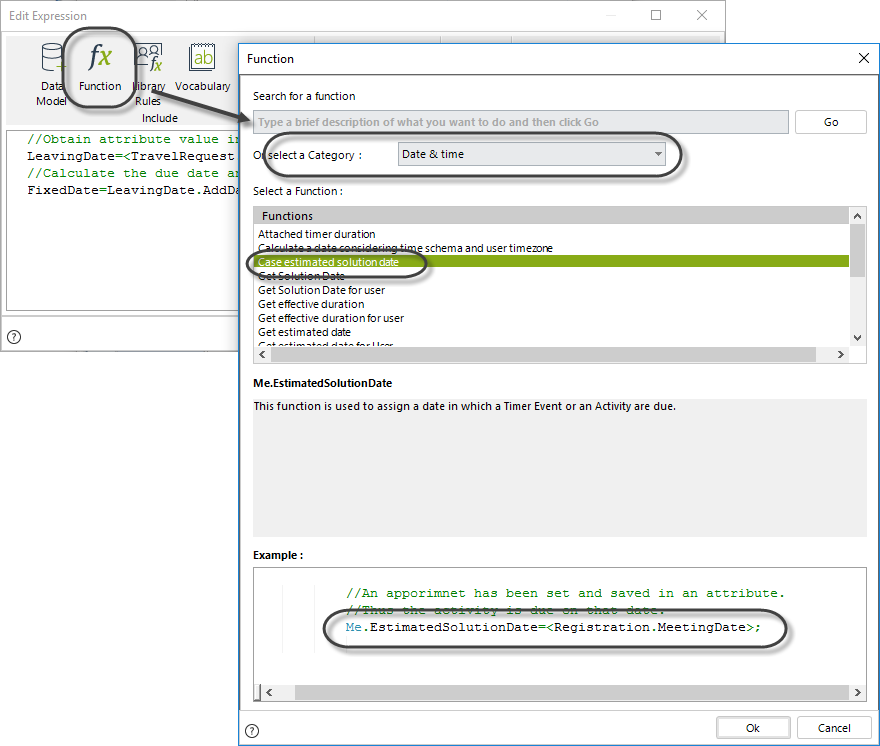
4. To set the duration to the Task use the function Case estimated solution date found in the Date & Time Category, as shown below.
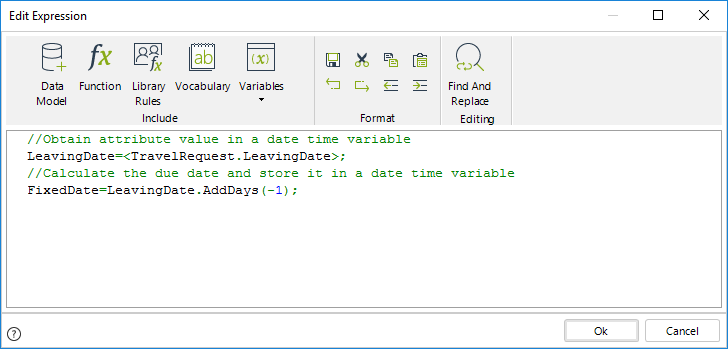
The next image shows the code of the expression:
//Obtain attribute value in a date time variable
LeavingDate=<TravelRequest.LeavingDate>;
//Calculate the due date and store it in a date time variable
FixedDate=LeavingDate.AddDays(-1);
//Assign Duration based on the calculated date.
Me.EstimatedSolutionDate=FixedDate;
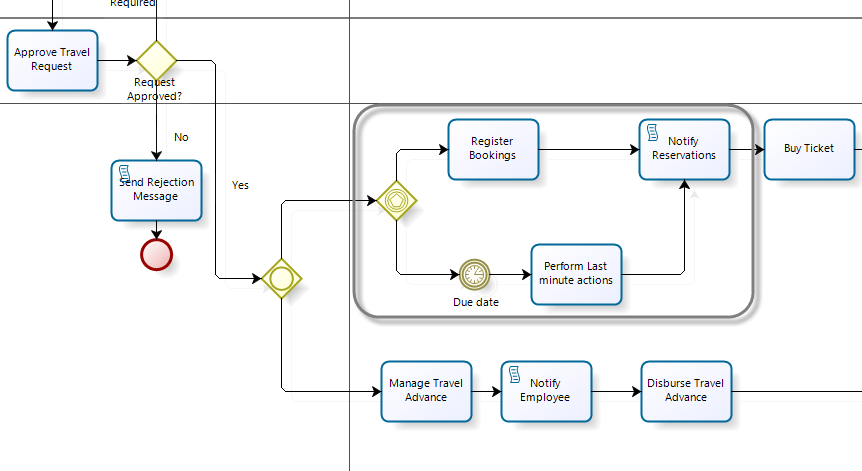
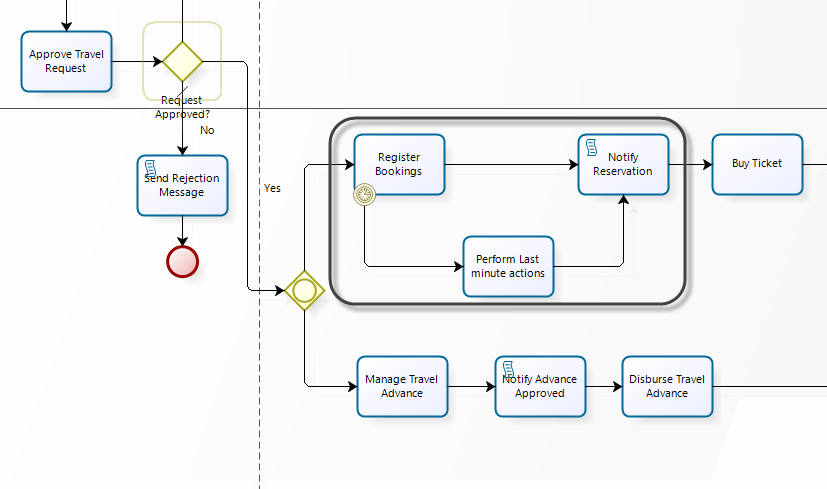
In the Travel Request process, suppose that once the booking flight due date has lapsed (one day before the trip), the booking administrator's supervisor must search for last minute flight offers.
You can use an Event based Gateway to evaluate if the Bookings Task has been reached before the booking due date. If the due date is reached first, the Bookings Task will be disabled and the Perform Last minute actions Task will be enabled for the supervisor (Boss).
|
It is recommend to avoid modeling synchronous automatic activities after a timer. See Timer modeling best practices. |
In order to configure the timer duration follow the next steps:
1. In the fourth step of the Bizagi Process Wizard (Business Rules), select Activity Actions.
Click on the Timer Event in which the duration will be calculated and create an On Enter Expression.
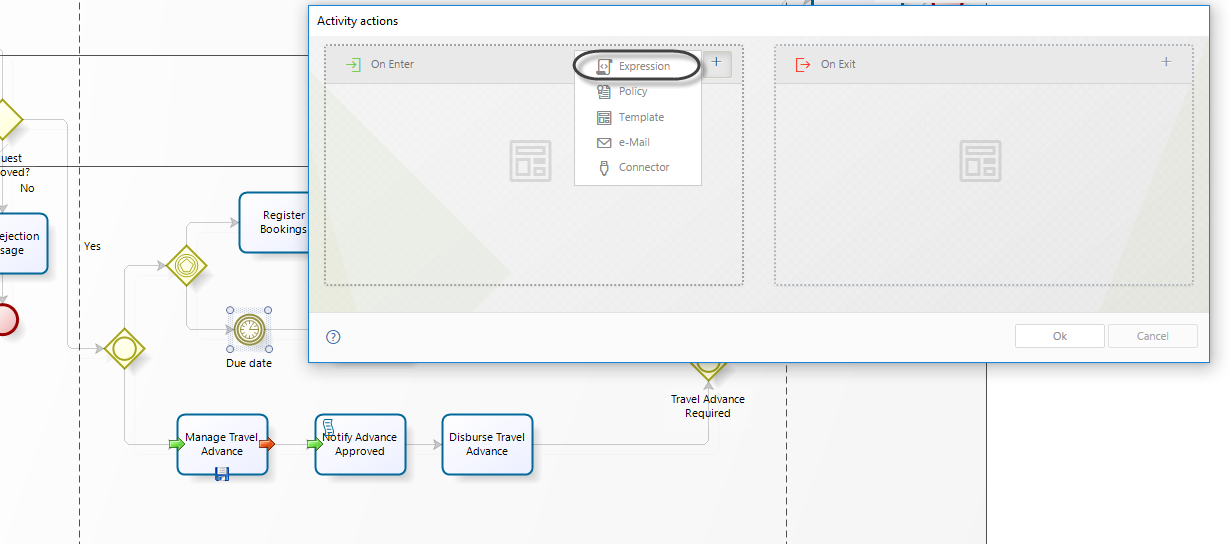
2. Declare the following variables:
•LeavingDate: Stores the value of the Leaving Date attribute.
•FixedDate: Stores the derived due date and will be used to set the Timer Duration.

3. Create the expression to set the duration.
First retrieve the leaving date from the attribute Leaving Date in the data model. This value will be set to the variable declared previously.

The Timer duration will be set to one day prior to the LeavingDate.
To obtain this fixed date we subtract one day from the date stored in the LeavingDate variable.
This result is then assigned to the FixedDate variable.

4. To set the duration to the Timer Event use the function Case estimated solution date in the Date & Time Category, as shown below.

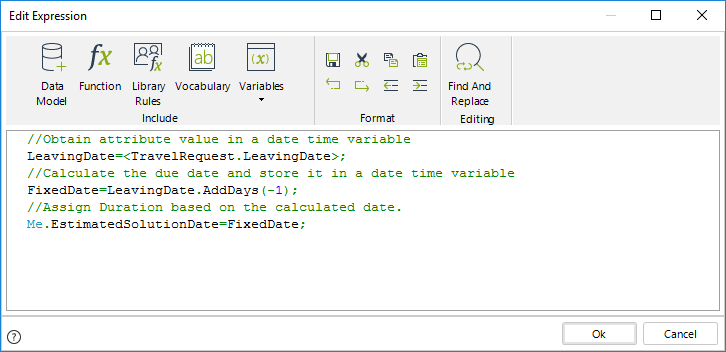
The expression code is as follows:

//Obtain attribute value in a date time variable
LeavingDate=<TravelRequest.LeavingDate>;
//Calculate the due date and store it in a date time variable
FixedDate=LeavingDate.AddDays(-1);
//Assign Duration based on the calculated date.
Me.EstimatedSolutionDate=FixedDate;
|
Timers durations are defined in the same way as Tasks durations. You can use either the Me.Duration (x minutes) or Me.EstimatedSolutionDate (a fixed date) function according to the Business conditions. |
Set duration to Timers attached to activities
In the Travel Request process, suppose the booking administrator must book the hotel and flight within three days of the request being made. If the due date is reached and the bookings are not done, the booking administrator's supervisor will have to perform the outstanding job(s) last minute.
This situation can be modeled by using a Timer Event attached to the Booking Task. See best practice in modeling when using timers attached events.
Events attached to the boundaries of an activity are used to activate exception flows according to defined Business conditions. When using Timer Event attached to activities, an exception flow is enabled once an specified time or a defined date is reached.
In this example, if the bookings are not finalized after three days, an exception flow is activated and the Perform Last Minute Actions Task is enabled for the booking administrator's supervisor. We need to define the timer's duration in order to properly model this business situation.
In order to configure the timer duration follow the next steps:
1. In the fourth step of the Bizagi Process Wizard (Business Rules), select Activity Actions.
Click on the Timer Event in which the duration will be calculated and create an On Enter Expression.
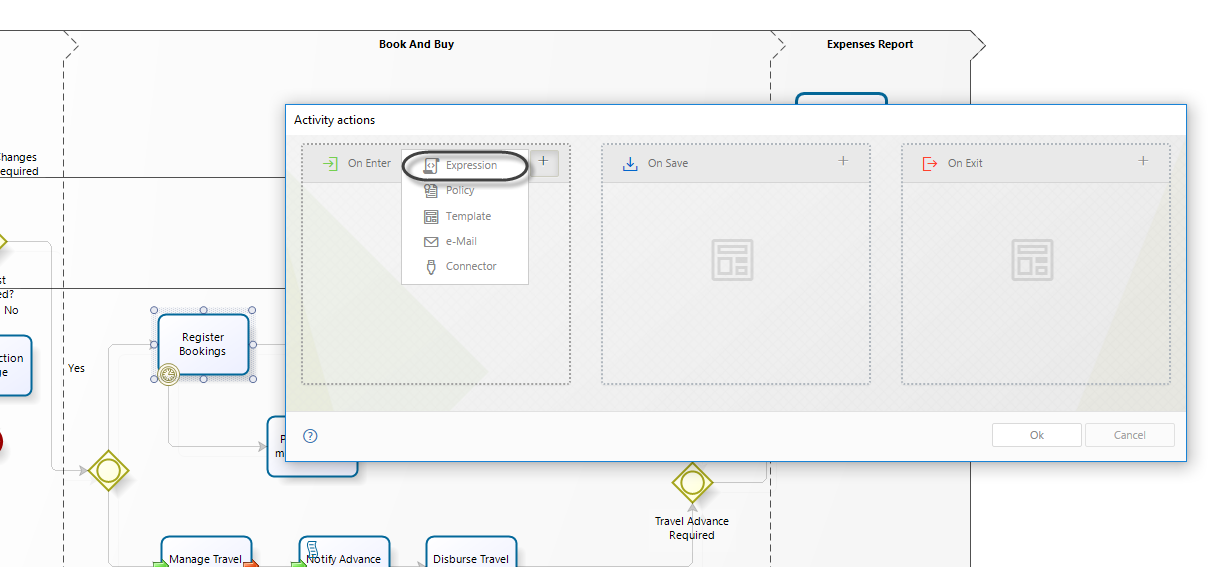
2. Create the expression to set the duration.
We recommend to use vocabularies to store constant duration for Tasks, to allow for easy modification in the Work Portal if the business condition should change.
In order to use vocabularies, they have to be created prior to the creation of the referencing expression.
A constant has been previously defined in the vocabulary for this purpose (BookingDuration). This duration can be modified at any time by end users in the Work Portal, to respond to changing business needs.
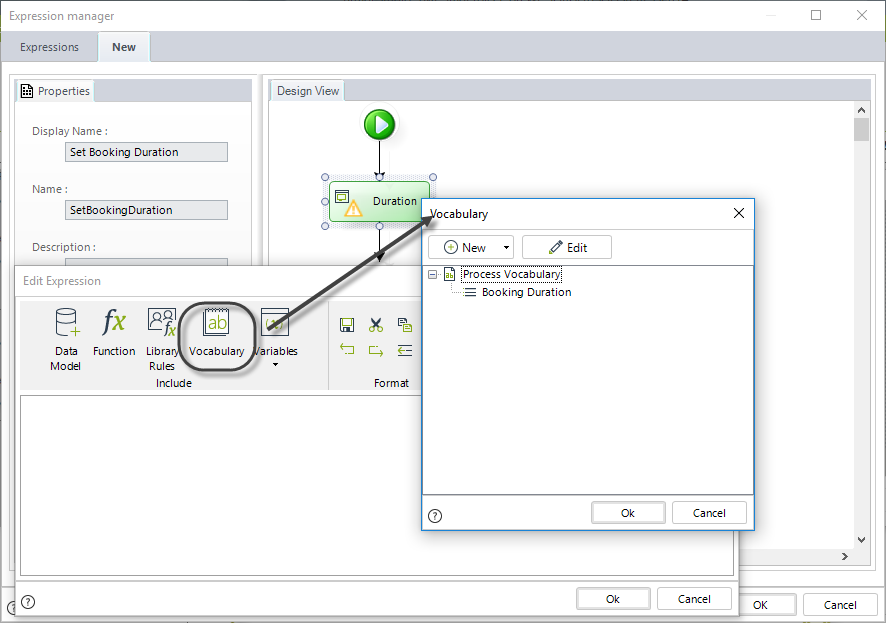
3. To set the duration for the Timer use the function Timer Event Duration.
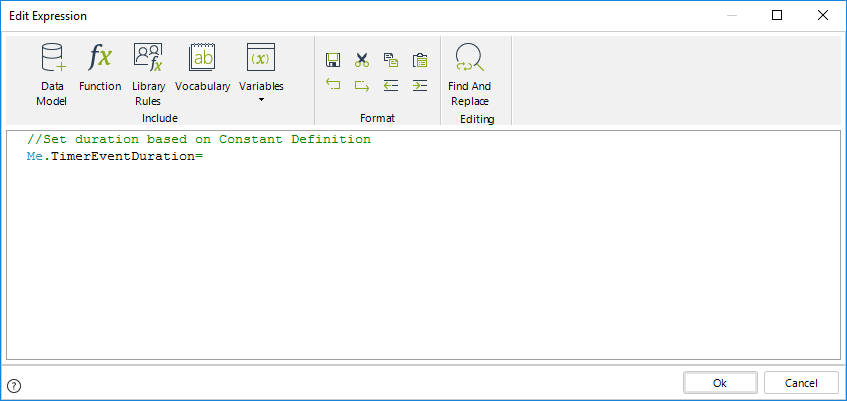
Obtain the constant defined in the vocabulary by using the ResolveVocabulary found in the Function list of the Miscellaneous Category, as shown below.
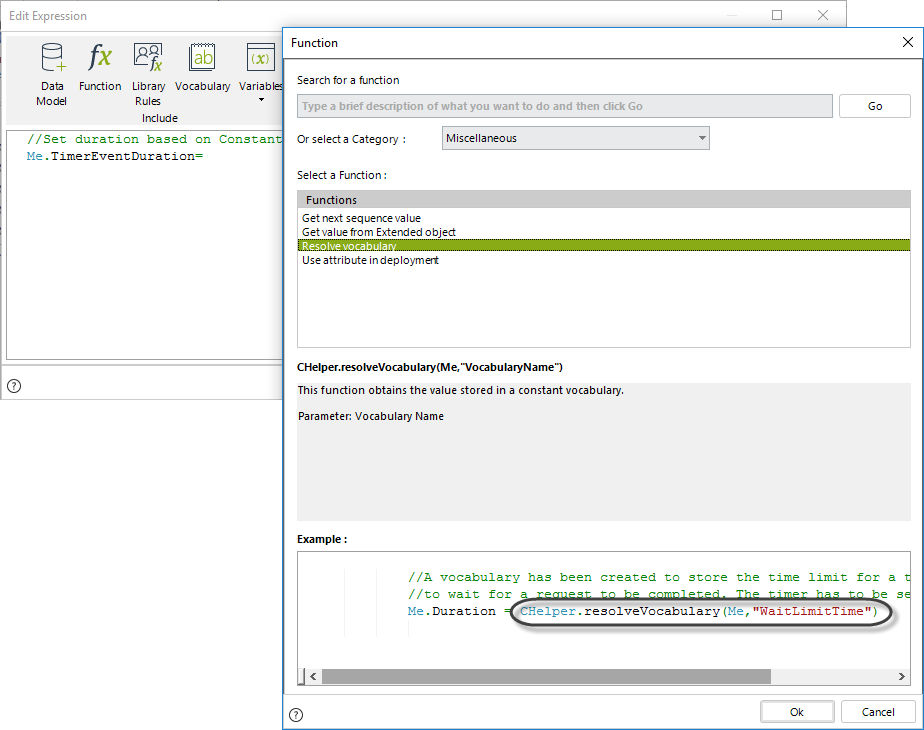
The next image shows the code of the expression:
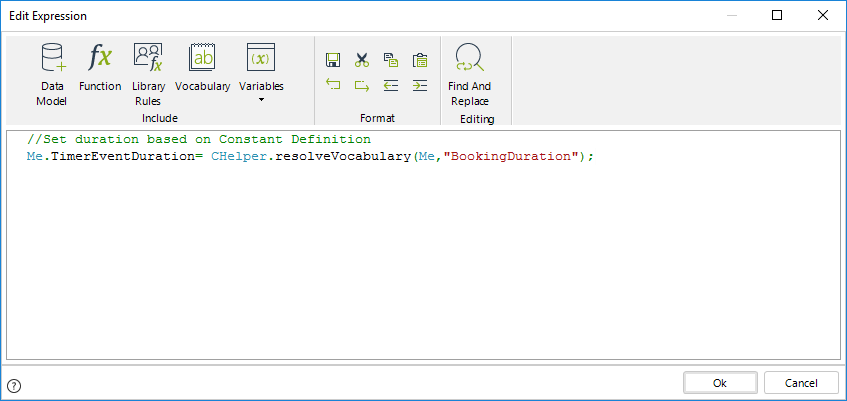
//Set duration based on Constant Definition
Me.TimerEventDuration = CHelper.resolveVocabulary(Me,"BookingDuration");
Set timer duration considering the Working time schema and the user's timezone
The Agility Corp manages the customer's claims and complaints using Bizagi. The company has established that a customer service agent can spend maximum 4 hours to respond a claim or a complaint. Agents work in with different shifts so the due date of the resolution of a task must be set considering the company's working time schema and the agent's timezone.
Bizagi uses a method called Me.EstimatedSolutionDate, that calculates the due date of an activity. However we will use it considering the timezone of the user.
1. In the fourth step of the Bizagi Process Wizard (Business Rules), select Activity Actions.
Click on the task for which the duration will be set and create an On Enter Expression.
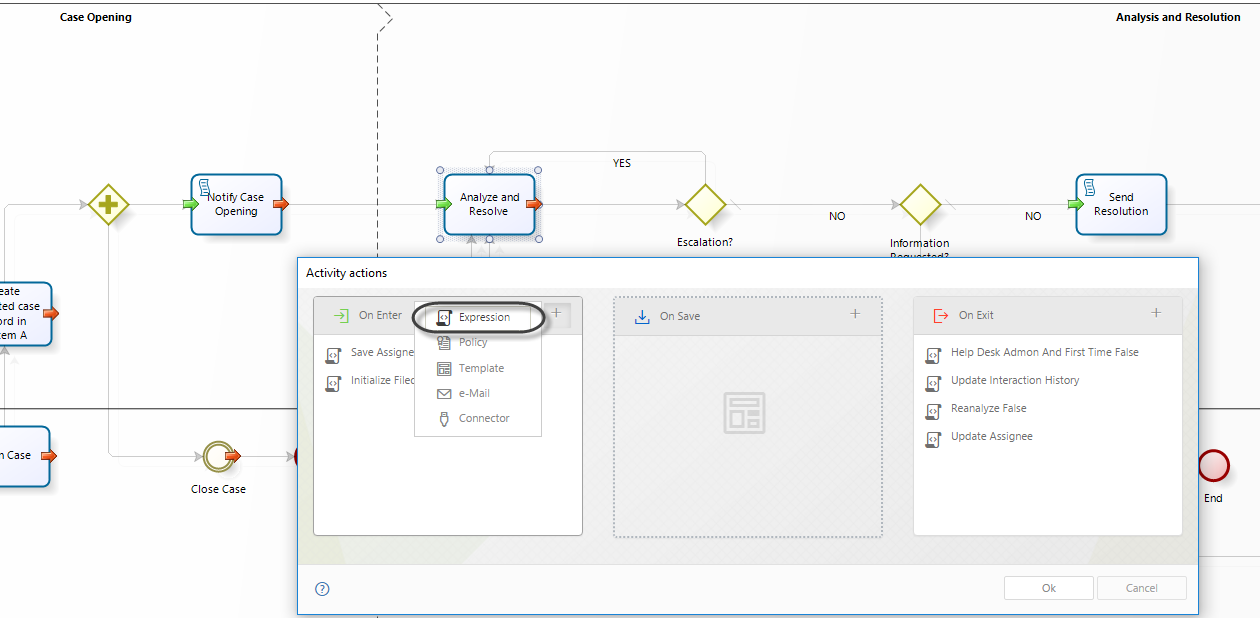
2. Create an expression.
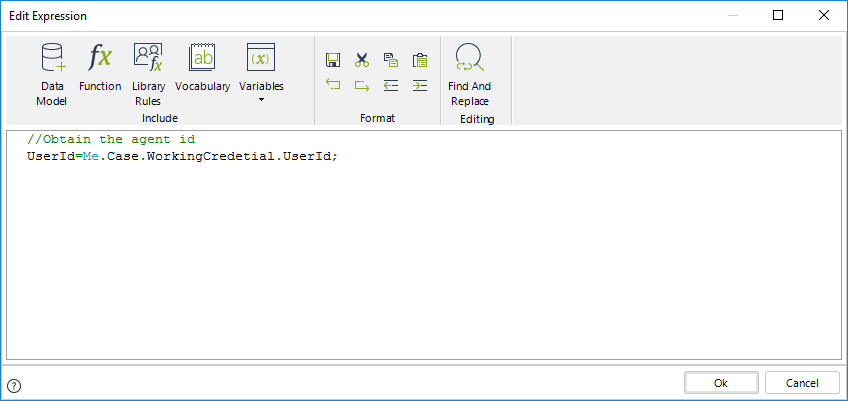
First we must obtain the agent's id using the function User id of the current user
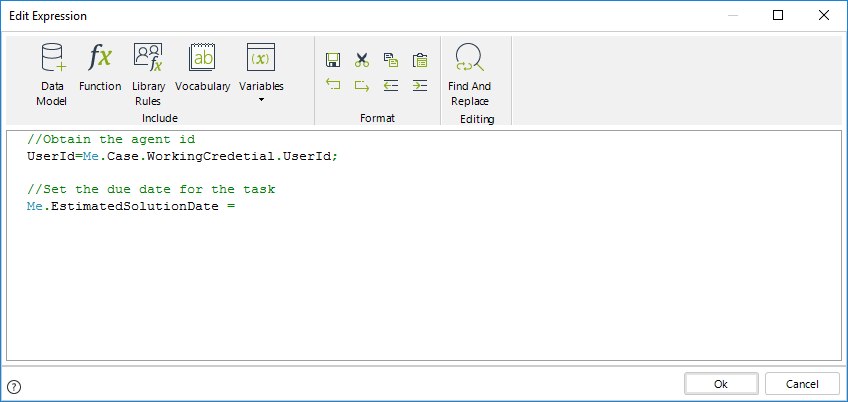
3. To set the duration to the task, use the function Case estimated solution date in the Date & Time Category
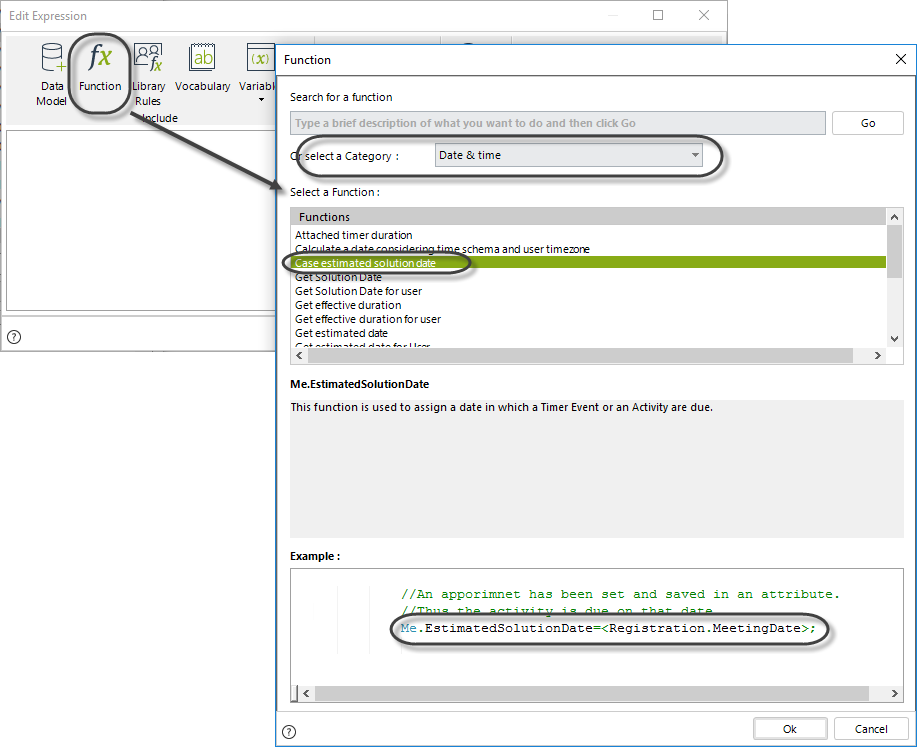
4. Use the function Calculate a date considering the time schema and user timezone to obtain the due date, considering the Working time schema and the agent's timezone.
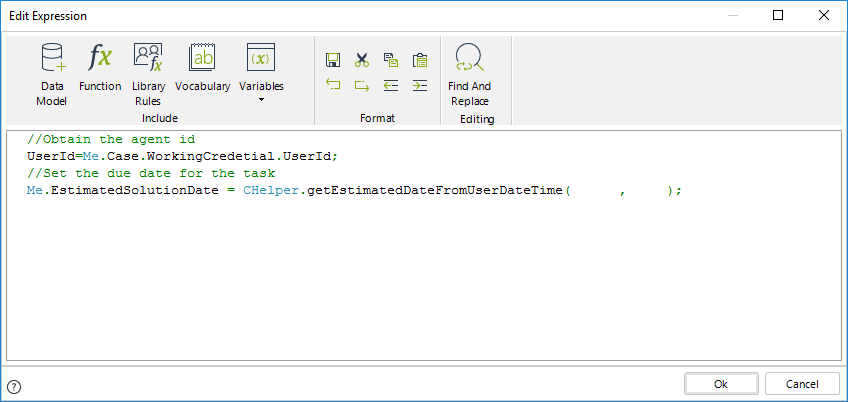
The syntax for the function is:
CHelper.getEstimatedDateFromUserDateTime(UserId,iDuration)
Include the parameters of the function. The first parameter is the id of the agent user that we previously obtained, and the second parameter is the time in minutes the agent has to complete the task.
The expression code is as follows:
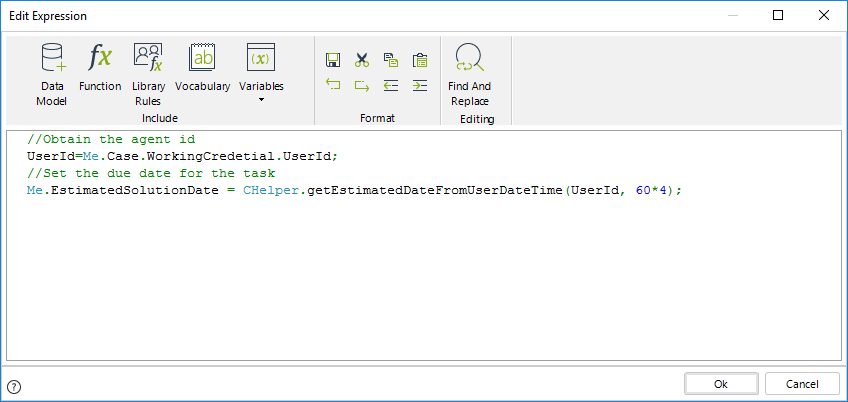
Note that the expression above converts days into minutes.
The conversion is needed as the iDuration parameter expects the duration in minutes. The total minutes in 4 hours is calculated using the formula: 60 minutes in an hour multiplied by 4 hours (i.e. 60*4)
//Obtain the agent id
UserId=Me.Case.WorkingCredetial.UserId;
//Set the due date for the task
Me.EstimatedSolutionDate = CHelper.getEstimatedDateFromUserDateTime(UserId, 60*4);
Last Updated 1/6/2022 4:16:19 PM