Overview
The Content Security Policy (CSP) is an HTTP header that adds an extra layer of protection to web pages by helping prevent common security attacks such as Cross Site Scripting (XSS) and Clickjacking. CSP allows you to control which types of resources—such as JavaScript, CSS, images, and more—can be loaded by the browser on a given page. In Bizagi, the CSP is used to define which resources are permitted when working with Widgets and Attended Bots. You need to configure a custom CSP if your solution includes components that load scripts from external URLs, embed content from third-party domains (e.g., iframes, images), send or receive data from external APIs or services. This article explains how to configure the CSP header within Bizagi Studio to securely enable content from these components.
Understanding Content Security Policy Directives and Source References
The CSP works by defining rules that control which resources can be loaded in the Work Portal. These rules are expressed as directives, each specifying a particular type of content and the sources from which it can be loaded. Directives are separated by semicolons and follow the format directive-name value. For example:
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; img-src 'self' example.com
This policy includes two directives:
•default-src 'self': allows everything but only from the same origin.
•img-src 'self' example.com: allows images to be loaded from the same origin and from example.com.
CSP enables you to allow or block specific content types—such as JavaScript calls or CSS components—based on your security requirements. The table below outlines the main directives available for configuring CSP in Bizagi. For a complete list, refer to the third-party documentation on official Content Security Policy.
Directive |
Description |
|---|---|
default-src |
Defines the default policy for fetching JavaScript, Images, CSS, Fonts, AJAX requests, Frames and Media resources. This directive basically works as a fallback for some of the other directives. However, not all directives fallback to it. |
script-src |
Defines valid sources of JavaScript. |
style-src |
Defines valid sources of CSSs or stylesheets. |
img-src |
Defines valid sources of images. |
connect-src |
Applies to XMLHttpRequest (AJAX), WebSocket, fetch(), <a ping> or EventSource. If not allowed, the browser shows a 400 HTTP code. |
font-src |
Defines valid sources of font resources. |
object-src |
Defines valid sources of plugins (<object>, <embed>, <applet>). |
media-src |
Defines valid sources of audio and video (<audio>, <video>). |
frame-src |
Defines valid sources for loading frames. |
Each directive can include one or more references, which specify the allowed sources. For a complete list, refer to the third-party documentation on official Content Security Policy. Common references include:
Reference |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
* |
Used as a wildcard. It allows any URL except the data:, blob: and filesystem: schemes. |
script-src *: |
'none' |
Prevents loading resources from any source. |
object-src 'none' |
'self' |
Allows loading resources from the same origin (host, and port). |
default-src 'self' |
data: |
Allows loading resources via the data scheme (e.g. Base64 encoded images). |
img-src data: |
specificDomain.com |
Allows loading resources from the specific domain |
media-src specificDomain.com |
*.example.com |
Allows loading resources from any subdomain under example.com. |
img-src *.example.com |
https: |
Allows loading resources only over HTTPS on any domain |
object-src https: |
'unsafe-inline' |
Allows use of inline source elements such as style attribute, onclick, or script tag bodies (depends on the context of the source it is applied to) and javascript: URIs |
script-src 'unsafe-inline' |
'unsafe-eval' |
Allows unsafe dynamic code evaluation such as JavaScript eval() |
script-src 'unsafe-eval' |
|
•When a directive includes multiple sources, separate them with spaces. •If 'none' is used, it must be the only value in that directive. •You don't need to include every directive in your CSP. It is recommended to always include default-src as baseline and add only the directives needed to grant access to specific resource types. •For example, if you need to grant access to a source that loads resources of the script-src, style-src, and img-src, include only those three directives in your policy. |
Default Content Security Policy in Bizagi Studio
By default, Bizagi defines the following Content Security Policy (CSP):
default-src 'self' data: blob:;
script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval';
style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline';
img-src 'self' data: blob:;
font-src * 'unsafe-inline' data: blob:;
This configuration allows resources from the same origin, permits inline scripts and styles, supports loading from data: and blob: URLs, and allows fonts from any source.
Customizing Content Security Policy for External Resources
When using Attended Bots or widgets that load content from external sources, the default CSP needs to be modified. Only the relevant directives should be updated based on the resource types used. To apply a custom CSP, you must configure it through Bizagi's Environment options. The next section explains how to define a new Content Security Policy in Bizagi Studio.
Content Security Policy for Attended Bots
When using Attended Bots, the CSP must include access to the orchestrator and local bot service:
default-src http://127.0.0.1:2323 [http://www.yourorchestrator.com] ‘self’ data: blob:;
script-src ‘self’ ‘unsafe-inline’ ‘unsafe-eval’;
style-src ‘self’ ‘unsafe-inline’ blob:;
img-src ‘self’ data: blob:;
font-src * ‘self’ ‘unsafe-inline’ data:;
Replace [http://www.yourorchestrator.com] with the actual URL of your orchestrator.
Content Security Policy for Widgets
Some widgets may require a specific Content Security Policy (CSP) configuration. You should configure CSP when your widget:
•Loads scripts from external URLs.
•Embeds content (e.g. iframes, images) from third-party domains.
•Sends or receives data from external APIs of services.
To determine the required directives and source references, consult the widget's documentation (see the Bizagi Xchange documentation for widgets downloaded from Widget XChange). If you are developing a custom widget, refer to the CSP Directives and CSP Source List Reference tables above, or consult the third-party documentation on official Content Security Policy. For example, if a widget requires access to scripts, styles, and images from external URLs, update only the relevant directives in Bizagi Studio:
default-src 'self' data: blob:;
script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' [widgetScriptURL];
style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' [widgetStyleURL];
img-src 'self' data: blob: [widgetImgURL];
Where:
•[widgetScriptURL]: URL from which the widget loads its scripts.
•[widgetStyleURL]: URL from which the widget loads its styles.
•[widgetImgURL]: URL from which the widget loads its images.
Content Security Policy for Multiple Resources
If your project includes multiple widgets or a combination of widgets and Attended Bots, you only need to define one Content Security Policy that includes all the required resources. For example, if you need to use one widget that uses the script-src, style-src and img-src directives; and the RPA bots, the Content Security Policy definition would be as follows:
default-src http://127.0.0.1:2323 [http://www.yourorchestrator.com] 'self' data: blob:;
script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' [widgetScriptURL];
style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' blob: [widgetStyleURL];
img-src 'self' data: blob: [widgetImgURL];
font-src * ‘self’ ‘unsafe-inline’ data:;
Where:
•http://127.0.0.1:2323 and [http://www.yourorchestrator.com] correspond to the Attended Bots configuration parameters. Bear in mind that you need to replace [http://www.yourorchestrator.com] with your Orchestrator's URL.
•[widgetScriptURL], [widgetStyleURL] and [widgetImgURL] correspond to the widget configuration parameters. Bear in mind that you need to replace this parameters with the URLs from which the widget loads its content.
Steps to Configure CSP in Bizagi Studio
To configure the Content Security Policy in Bizagi Studio, complete the following steps:
1.In Bizagi Studio, go to the Configuration tab and select Environment.
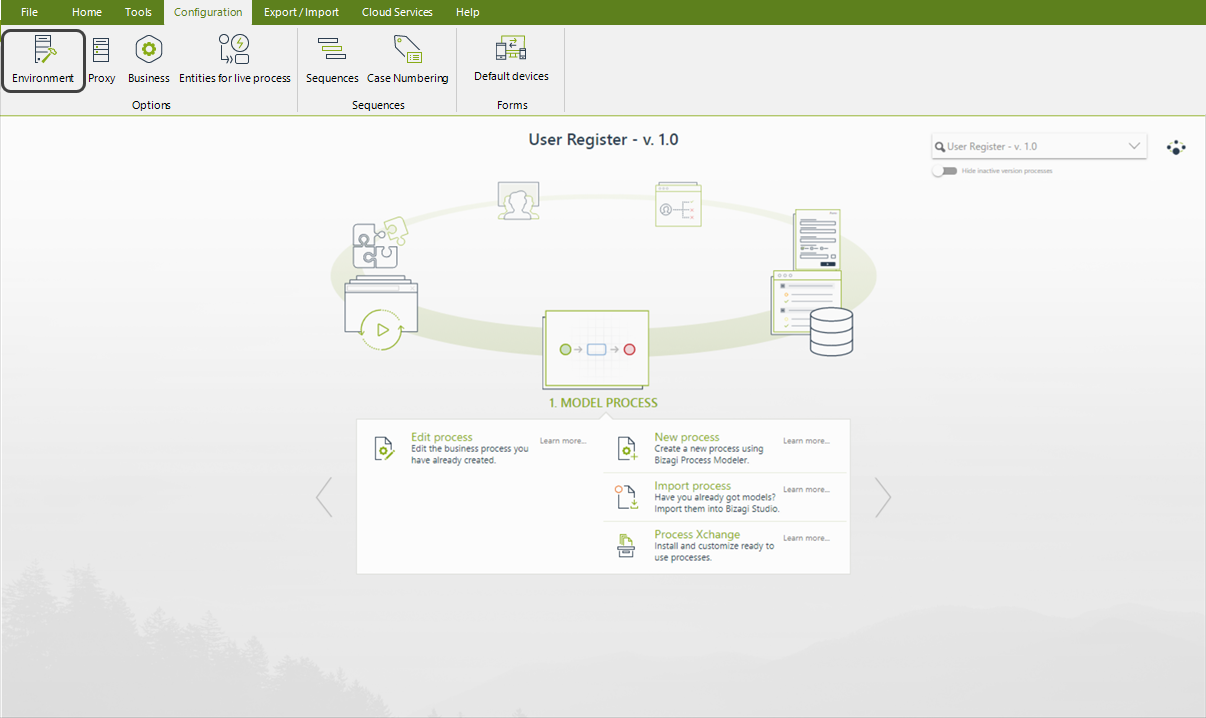
2.In the new window, go to the custom tab. Here, you can define new custom parameters for each of the environments. Click the New button to create a new custom parameter.
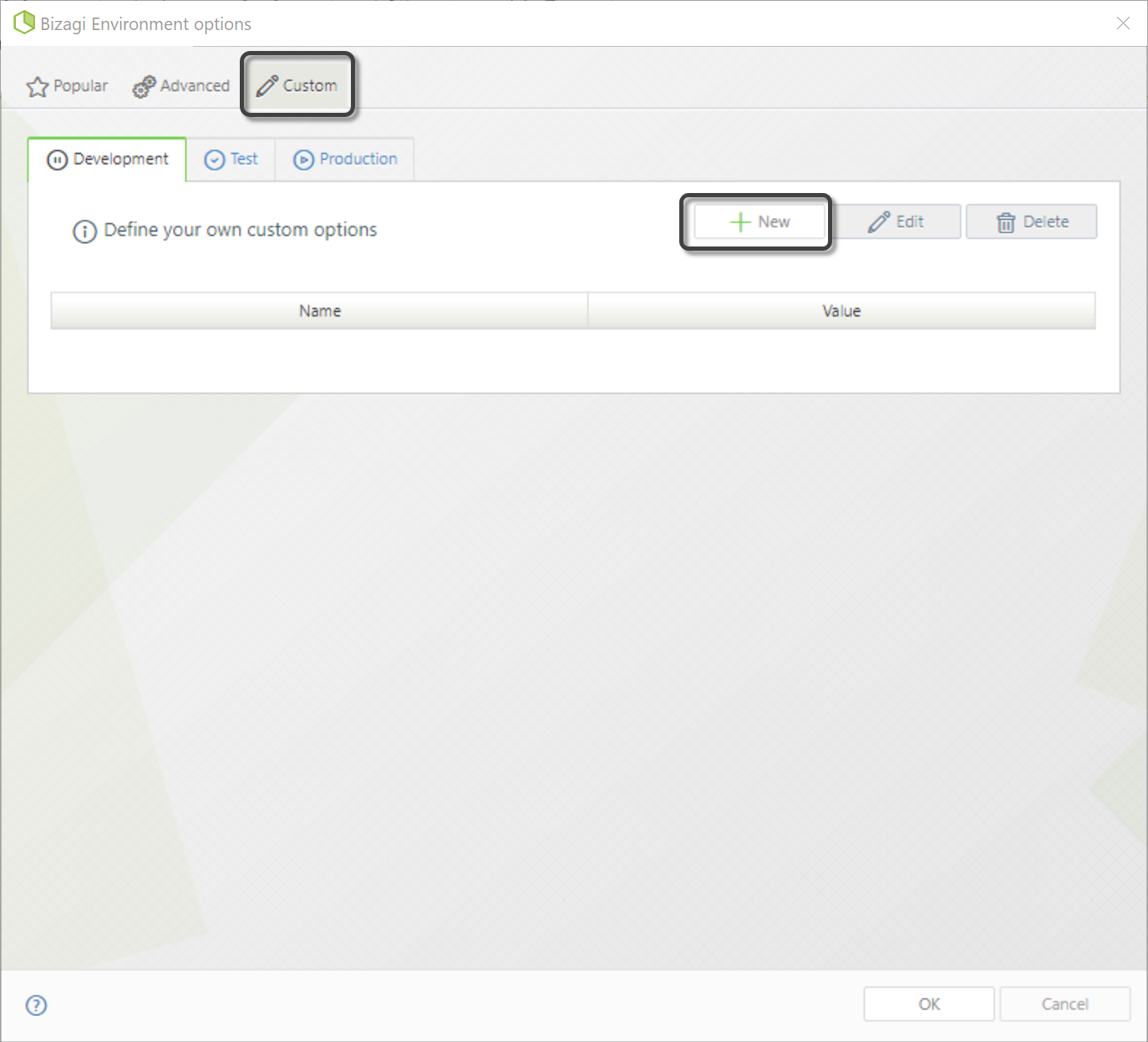
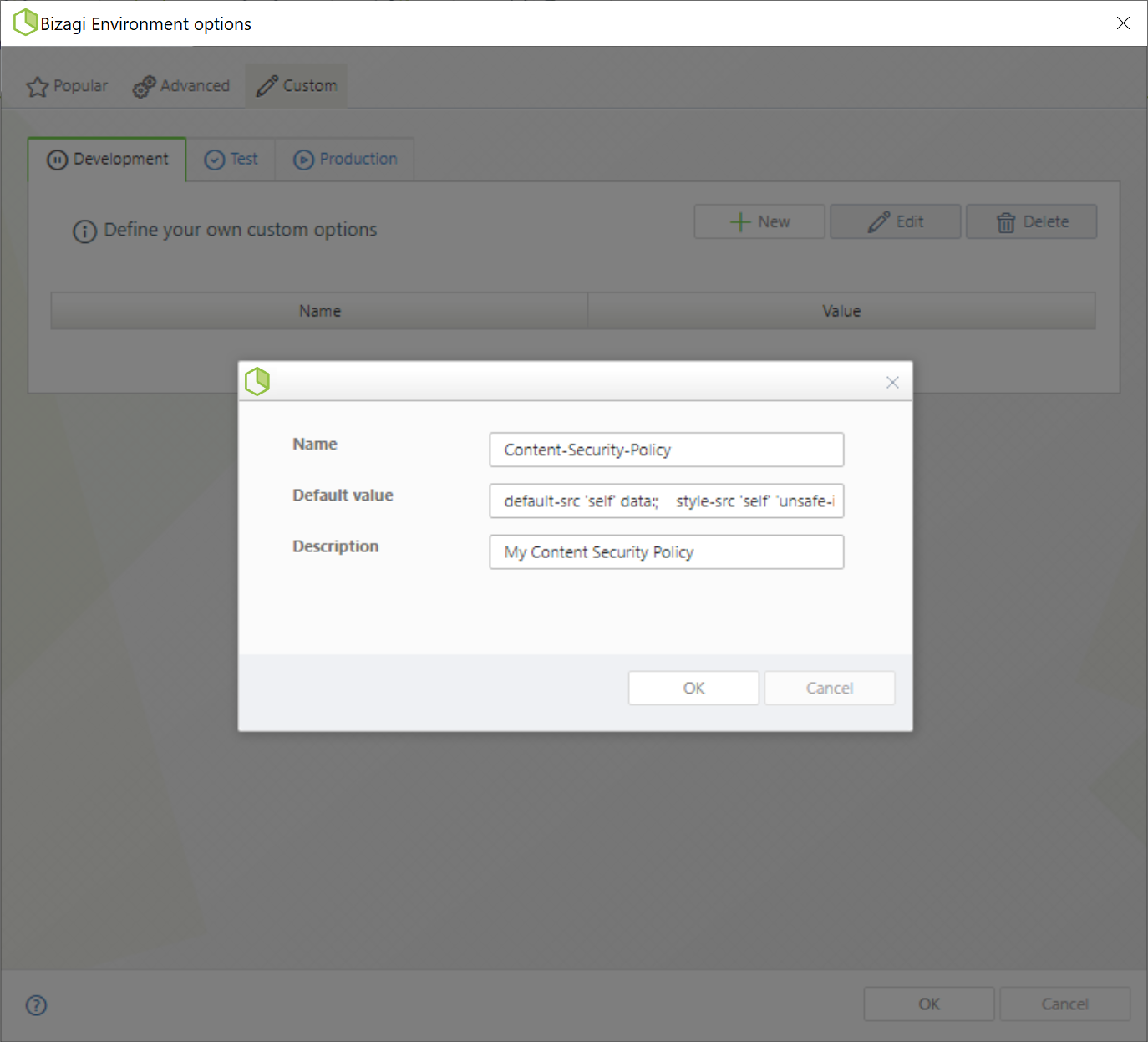
3.When creating a new parameter, you must define a name, a value and a description. To configure the Content Security Policy, use the following parameters:
oName: Content-Security-Policy.
oDefault value: use a valid content security policy definition, depending on whether you are going to use an Attended Bot or a Widget.
oDescription: a description for your new parameter.
|
Make sure to define correctly the Content Security Policy. If the value of the parameter has an incorrect syntax, the parameter will be ignored and the policy will allow unrestricted access. |
4.When you finish, click OK. The new parameter will be shown in the corresponding environment.
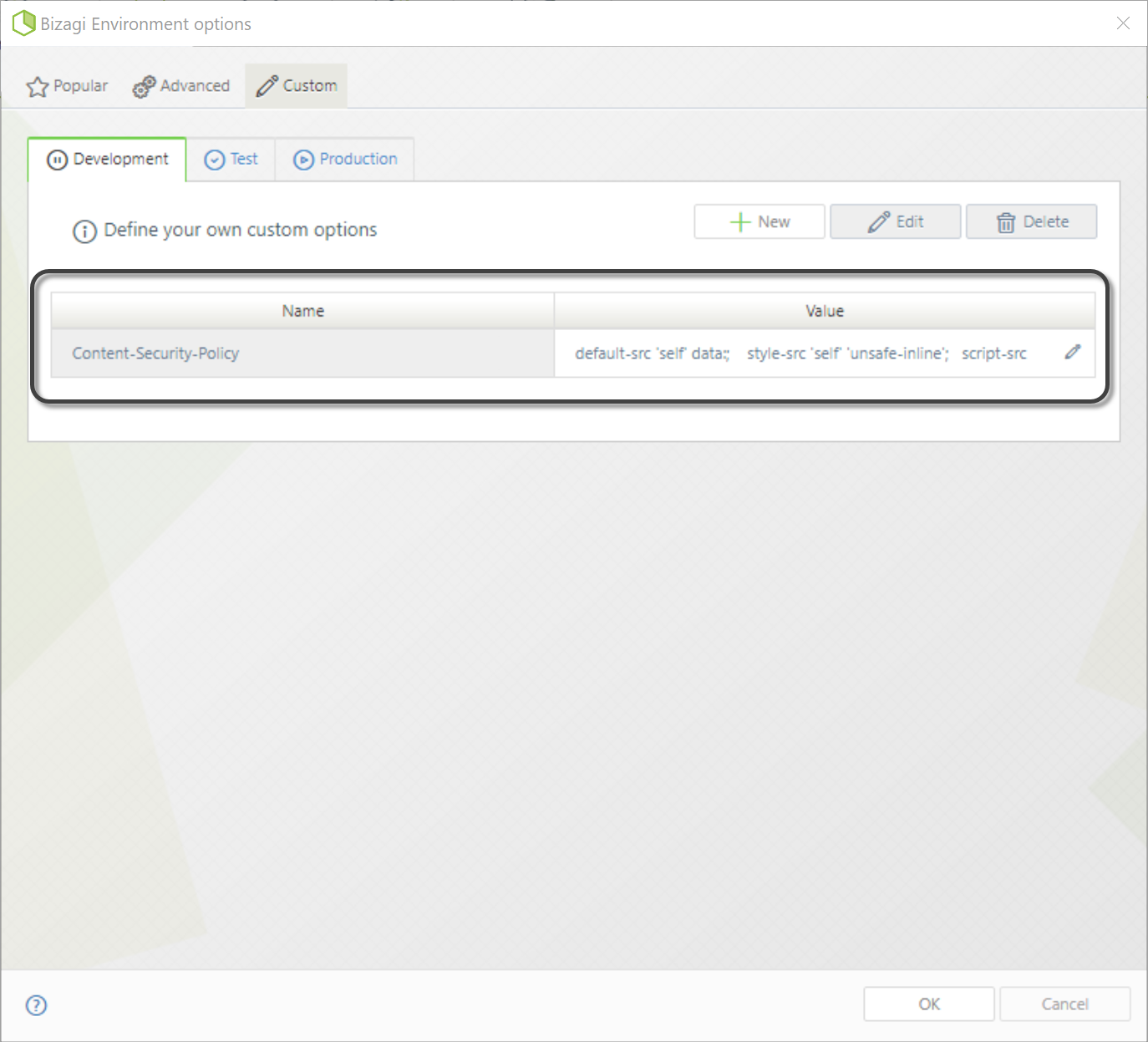
|
The Content Security Policy settings are environment-specific. You must configure the CSP separately for each environment during deployment, using the appropriate tab in the configuration panel. |
Considerations for CSP Configuration
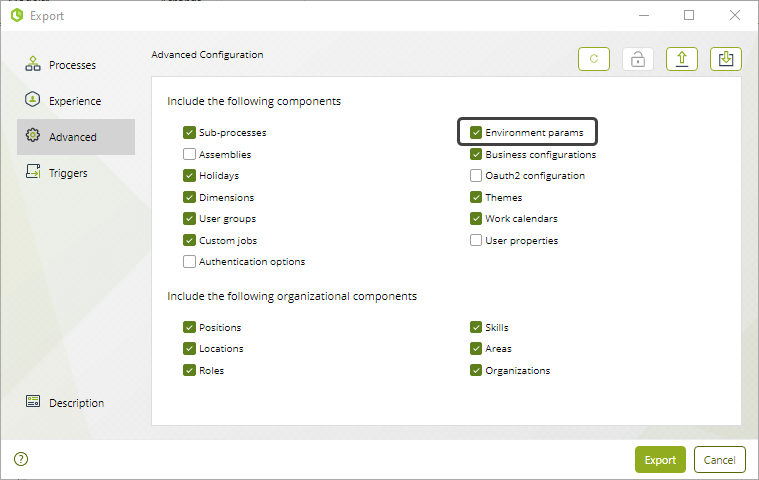
To ensure the Content Security Policy is exported correctly, open the Advanced settings in the export window and check the Environment Parameters property box. Then, complete the configuration by following these steps:
1.In Bizagi Studio navigate to the Export/Import tab and select Export
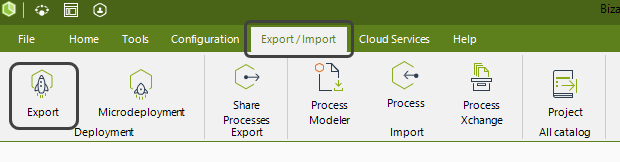
2.In the new window, go to the Advanced section and check the Environment Parameters property box.
|
Important conditions to consider when deploying CSP settings: •During the first deployment, the CSP configuration will be applied to the target environment. •If no manual changes have been made to the CSP in the target environment, any updates included in a new deployment package will overwrite the existing configuration. •If the CSP has been modified directly in the Test or Production environments using the Management Console (MC), future deployment packages containing CSP changes will be ignored. From that point on, all CSP updates must be made exclusively through the MC. |
Next steps
Once you have finished the Content Security Policy configuration, you can install your Widgets, or configure your Attended Bots.
Last Updated 10/7/2025 11:50:36 AM