Overview
Process modeling is usually performed by business analysts based on multiple sources of information, such as internal procedure guides or senior employees' experience. This could lead to an approximation of the process that does not necessarily reflect its reality
Thus there are two types of approaches of processes: theoretical (To-Be) and real (As-Is). The theoretical version represents the ideal, perfect process, in other words, the process as it is designed in theory. This version is very simple and easy to execute. On the other hand, the real version reflects the actual process flow with all its deviations and complexities, which occur in real-life operational processes.
Process Mining allows the visualization of all the possible ways to perform a process, both the theoretical and the real ones, reflecting a full picture of activities as they were actually performed. With this perspective, the business analysts of the company can perform deeper studies of different variants of the process to identify delays or reworks. To do this, Process Mining takes all the process information (event logs from activities) stored within the operational systems of the company, such as purchasing systems within a retail company, and makes them available for the company's analysts so that they can create models that correctly reflect the reality of the company's processes.
Within the event logs there is plenty of valuable information waiting to be used to improve the processes of the company. For this reason, there are multiple Process Mining analysis techniques that are classified into three main categories: Process Discovery, Conformance Checking, and Process Enhancement. Bizagi Modeler focuses on Process Discovery to help companies model processes from event logs.
Bizagi Modeler Process Discovery
Bizagi Modeler Process mining feature is focused on Process Discovery, this step encompasses the creation of a process model based on the analysis of an event log. These event logs, as explained above, are the day to day tasks of the company recorded and contains the case and activity information (identification numbers and dates).

One event is the execution of an activity of a particular process. Each event contains information on the duration of each activity and the log contains all the activities executed. For example, an event log contains all the activities performed in loan requests in a bank.
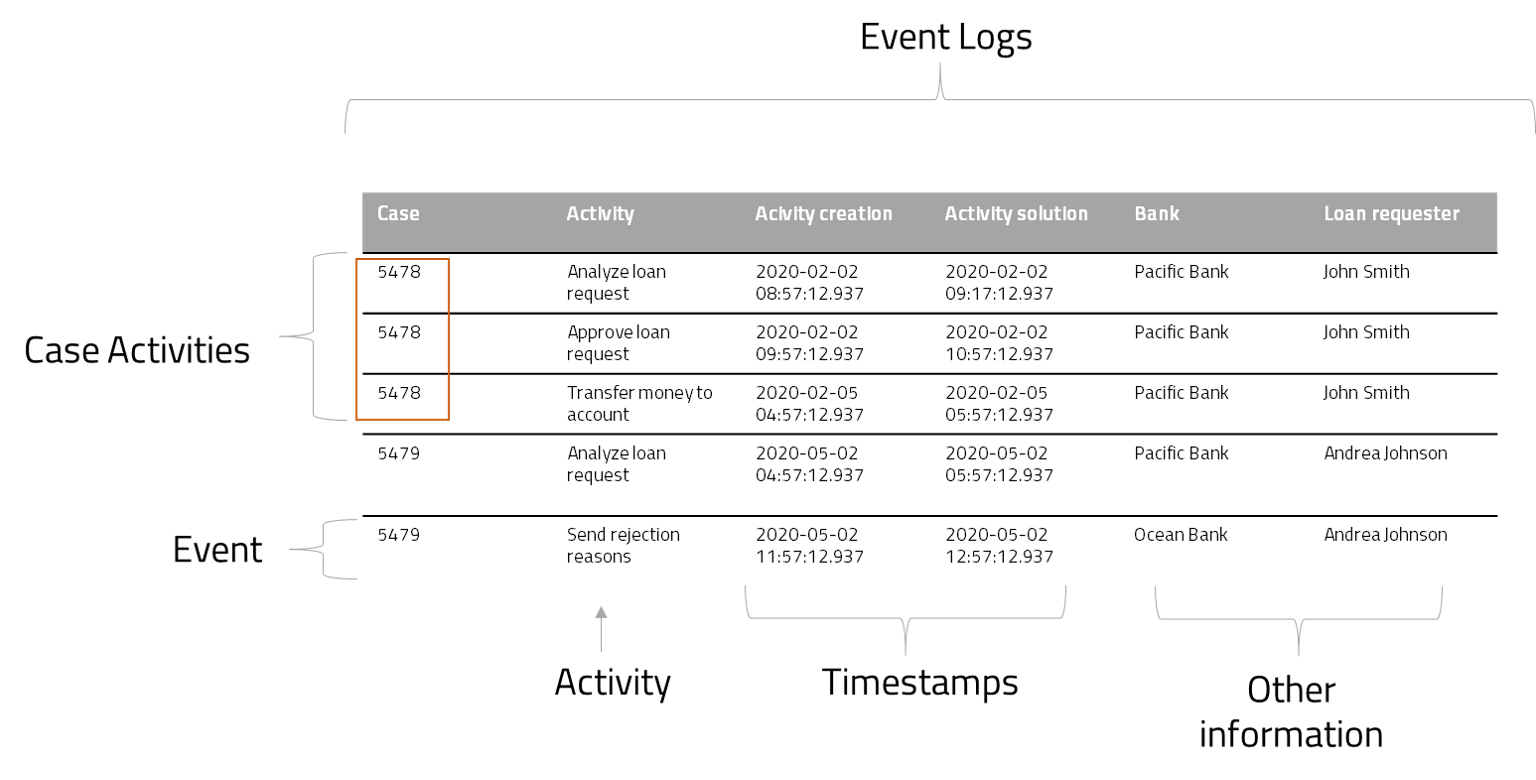
With process mining techniques, Bizagi Modeler can discover all the possible flows from all the multiple cases registered log, and start building a BPMN model, for example, from the previous image, the process mining identifies flows between activities, and build a model. With artificial intelligence analysis, Bizagi can build a resulting BPMN model, considering all possible flows:
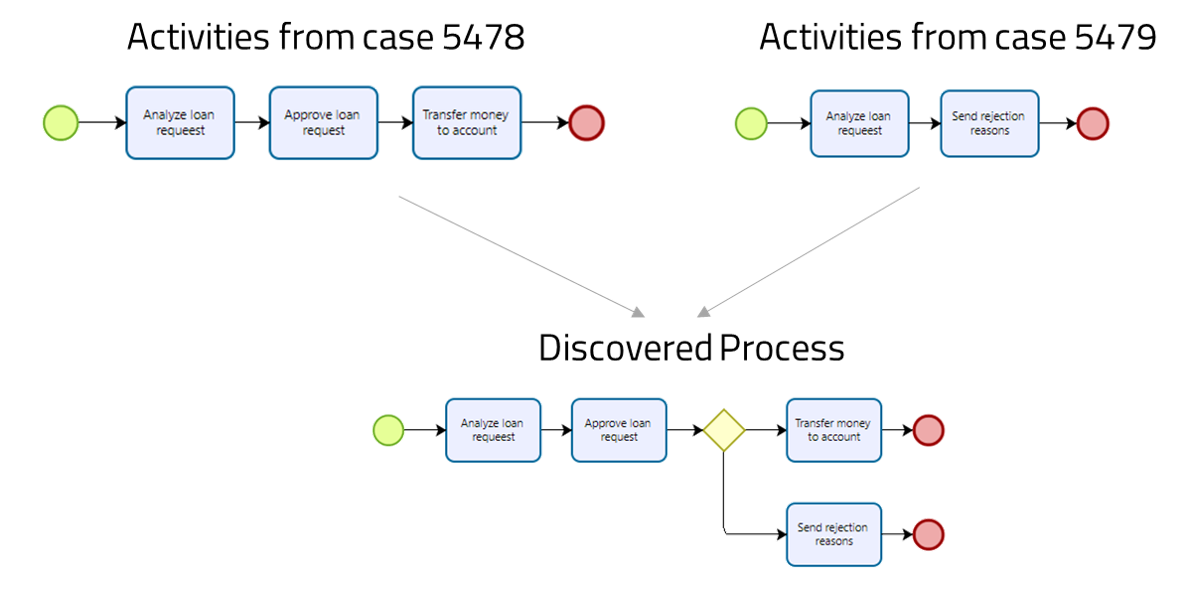
Process Mining is able to include other BPMN elements that reinforce the logic of your process, like gateways, when you have exclusive paths.
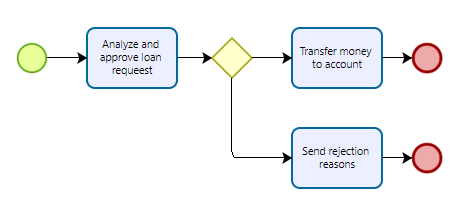
Sometimes, you need to modify the number of tasks, because you need to focus only on main tasks. Other scenarios imply that you must consider tasks being executed in parallel, or that you want to reduce the number of flows. Therefore, Bizagi Process Mining offers abstraction settings, or variables, that you can modify to generate other possible flows, based on the number of tasks or flows that you want to execute.
For example, you can simplify your model into 3 tasks:
Next Steps
Learn how the Bizagi Process Mining helps you to discover processes using event logs.
Last Updated 1/7/2022 2:14:36 PM