Overview
This article explains how you can interact with SAP OData services through the Bizagi Dispatcher deployed on SAP BTP by using any HTTP client or API testing tool. Each section guides you through the necessary steps so that you can request an authentication token from XSUAA and then use that token to perform read (GET) and write operations (POST, PATCH, DELETE) on the SAP services exposed to you.
Before you begin working with the Bizagi Dispatcher, it is important to understand how it interacts with SAP BTP and why it requires authentication tokens. The Dispatcher is a service deployed in SAP BTP that receives your requests and securely forwards them to the SAP destination that has been configured for you. When you use the Dispatcher, you do not need to manage SAP connectivity or handle SAP‑specific security settings yourself; the Dispatcher takes care of validating your credentials, handling secure communications, and routing your requests to the correct SAP OData service.
All requests sent through the Dispatcher must be authorized, and that authorization is handled through XSUAA, the SAP Authorization and Trust Management Service. XSUAA is responsible for issuing OAuth2 tokens that confirm your identity and permissions. When you request a token, you authenticate using a Client ID and Client Secret, and XSUAA responds with an access token that you attach to all your requests. This token allows the Dispatcher to validate who you are and determine whether you are allowed to access the SAP system.
Before you start
Before you send your first request using your HTTP client or API testing tool, confirm that you have all the information required to complete the process successfully. Each of the following elements plays a key role in authentication or request routing:
•URL of the XSUAA authentication service, which you will use when requesting your token.
•Client ID and Client Secret assigned to the technical application that authenticates your requests.
•URL of the Bizagi Dispatcher, which receives and routes your calls.
•Name of the destination configured in SAP BTP that points to your SAP system.
•Path of the SAP OData service that you intend to consume.
•You need an HTTP client or API testing tool installed on your computer (e.g., Bruno, Postman, etc.).
Where to find your authentication credentials
If you do not yet know your authentication details, obtain them directly from SAP BTP by following these steps:
1.Open the SAP BTP Cockpit and navigate to the Subaccount where the Bizagi Dispatcher is deployed.
2.Go to the Spaces section and select the space that contains the Dispatcher.
3.Open Services > Instances to view the list of available service instances.
4.Locate the XSUAA instance associated with the Dispatcher, which contains the authentication credentials required for this process.
5.Select View Credentials or Service Key. The system displays the values named clientid, clientsecret, and url, which correspond to your Client ID, Client Secret, and Authentication URL. Copy these values carefully and store them securely, because you will need them when requesting your token.
Step 1: Request your authentication token
To start interacting with SAP through the Dispatcher, request an OAuth2 token from XSUAA.
1.Open your HTTP client and create a new request.
2.Set the HTTP method to GET.
3.Enter the authentication URL provided in your XSUAA credentials. The URL must follow this structure:
https://{subaccount}.authentication.{region}.hana.ondemand.com/oauth/token?grant_type=client_credentials
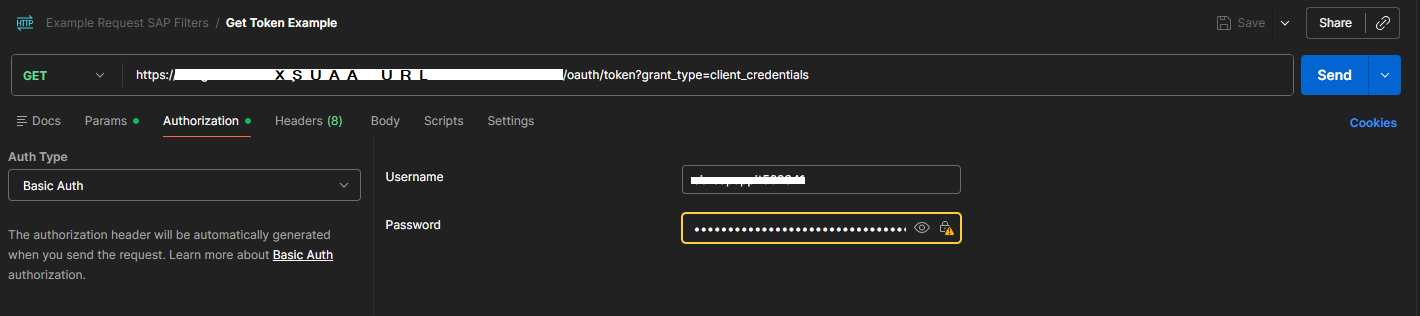
4.Open the Authorization tab and select Basic Auth as Auth Type.
5.Enter your Client ID in the Username field.
6.Enter your Client Secret in the Password field.
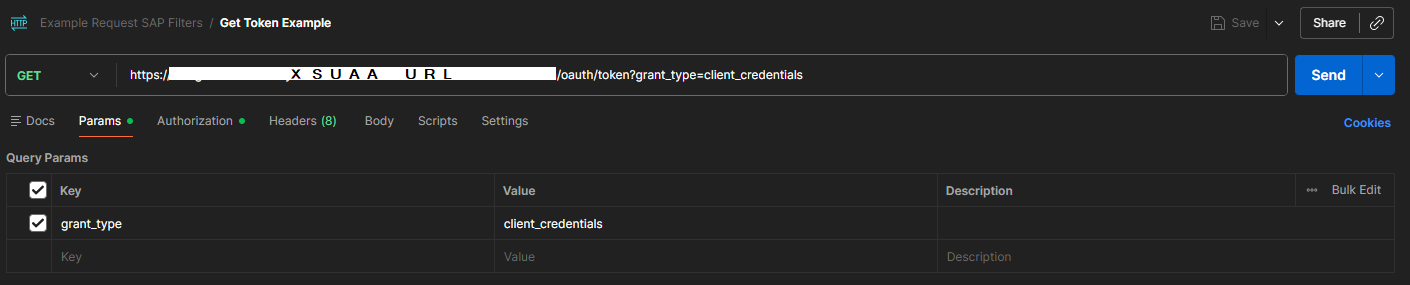
7.Open the Params tab and verify that the parameter grant_type is set to client_credentials.
8.Send the request. If your credentials are correct, your tool displays a successful response with Status: 200 OK.
9.The response body contains a JSON object where you will find the access_token field, which holds the token required for all subsequent requests, so copy this value and store it securely because you will use it in every request you send to the Dispatcher.
Example of a typical JSON response:
{
"access_token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJqaWQiOiJOcDBta...",
"token_type": "bearer",
"expires_in": 43199,
"scope": "uaa.resource",
"jti": "730f0fd73cac4872b18ccc5f6927c209"
}
|
The token includes an expiration time in the expires_in field, expressed in seconds; in the example above, the token expires in 43,199 seconds (approximately 12 hours), so you must request a new token when it expires. |
Step 2: Execute GET requests
With your access token ready, you can begin retrieving data from SAP.
Execute a GET All request
1.Create a new request in your HTTP client and open the Authorization tab.
2.Select Bearer Token and paste your access token into the Token field.
3.Enter the Dispatcher URL in the following format:
https://{dispatcher-url}/dispatcher?destination={destination-name}&path={odata-service-path}
4.Open the Params tab and verify that the destination and path parameters contain the appropriate values. For example:
Parameter |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
destination |
YourSAPDestination |
Exact name of the SAP destination defined in SAP BTP. |
path |
/.../YourEntitySet |
OData Entity Set path you want to query (without ID). |
|
The Dispatcher validates the path parameter strictly. Make sure the path does not include unsafe characters or multiple consecutive slashes (//). If the Dispatcher detects invalid characters or unsafe formatting, it rejects the request for security reasons. |
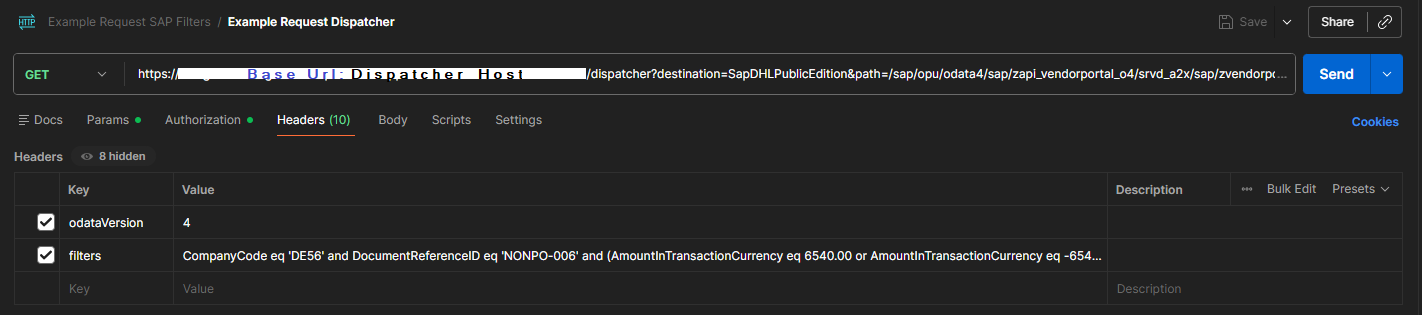
5.Open the Headers tab and add a header named odataVersion with the value 2 or 4, depending on the OData version used by the SAP service.
|
If the SAP service you are consuming supports OData V4, use version 4 because it offers better performance and improved capabilities compared to V2. |
6.If you need to filter the results, add a header named filters and enter a valid OData expression. Filters allow you to limit the returned data to only the records that meet your criteria. For example:
•CompanyCode eq '1000': filters the results by company code.
•Amount gt 500: filters the results by a numeric value greater than 500.
|
If your filter contains spaces, punctuation, or other special characters, encode the entire expression using URL encoding. This is required so that the Dispatcher can interpret your filter correctly. |
7.Send the request and review the response. The data field in the response contains the SAP payload as a JSON string, which you may need to parse depending on your use case.
Execute a GET by key request
If you need to retrieve a single specific record, include the key structure in the path parameter.
•For OData V2 services, use a format such as:
YourEntitySet('KEY')
•For OData V4 services, use a format such as:
YourEntitySet(FieldA='1000',FieldB='ABC')
|
Consult the $metadata document of the SAP service if you are unsure about the key structure. |
Step 3: Execute write operations
You can also perform write operations through the Dispatcher. These operations use the same Dispatcher URL and parameters as GET requests but require appropriate HTTP methods and JSON bodies.
Create a record (POST)
1.Set the HTTP method to POST.
2.Keep the Dispatcher URL and parameters identical to your GET request.
3.Open the Headers tab and add the headers Content-Type: application/json and odataVersion with the correct value.
4.Open the Body tab, select raw, choose JSON, and enter the new record using the required "d" wrapper. For example:
{
"d": {
"CompanyCode": "1000",
"Description": "New Item",
"Amount": 500.00
}
}
5.Send the request.
Update a record (PATCH)
1.Set the method to PATCH.
2.Include the entity key in the path parameter.
3.Enter only the fields you want to update, wrapped inside "d".
4.Send the request.
Delete a record (DELETE)
1.Set the method to DELETE.
2.Include the entity key in the path parameter.
3.Do not include a request body.
4.Send the request.
Function Imports and Action Imports
Some SAP OData services expose special operations known as Function Imports or Action Imports. When calling one of these operations, indicate this to the Dispatcher:
1.Add a header named isFunctionImport with the value true.
2.Enter any required parameters inside the "d" wrapper if the operation expects input.
3.Use the HTTP method defined by the OData service and send the request.
Troubleshooting
If something goes wrong, here are the most common issues and how to solve them:
Error |
Likely cause |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
401 Unauthorized |
Your token is invalid or expired. |
Request a new token and try again. |
403 Forbidden |
You may be missing permissions (scopes). |
Contact your administrator to confirm your access rights. |
404 Not Found |
The destination or the path may be incorrect. |
Verify that both values are spelled correctly. |
502 Bad Gateway |
There may be a connectivity issue between SAP BTP and the SAP system. |
Ask your administrator to check the connection. |
OData Syntax Error |
Your filter or path may contain a mistake. |
Review the syntax and apply URL encoding if needed. |
Last Updated 2/3/2026 8:48:51 PM