Overview
To make sure accurate diagrams, it is important to familiarize yourself with BPMN process modeling standard.
The following is a brief explanation of the BPMN Shapes.
BPMN Standard Shapes
The graphical aspects of BPMN is organized into specific categories.
Activities
Activities represent work or tasks carried out by members of the organization. They stand for manual or automatic tasks (performed by an external system or user). Activities can be atomic or non-atomic (compound) and they are classified into tasks and Sub-Processes.
Tasks
A task is an atomic Activity and used when the work in progress cannot be broken down to a finer level of detail. It is performed by a person and/or application.
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
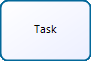
Task |
Is an atomic Activity within a Process flow. It is used when the work in the Process cannot be broken down to a finer level of detail. |
|
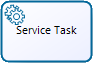
Service Task |
Is a Task that uses some sort of service that could be a Web service or an automated application. |
|
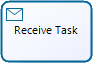
Receive Task |
Is a Task designed to wait for a message to arrive from an external participant (relative to the Process). |
|
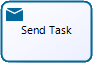
Send Task |
Is a Task designed to send a message to an external participant (relative to the Process). |
|
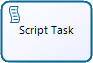
Script Task |
Is a Task that is executed by a Business Process Engine. The modeler defines a script in a language that the engine can interpret. |
|
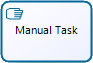
Manual Task |
Is a Task that is expected to be performed without the aid of any business process execution or any application. |
|
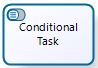
Conditional Task |
These tasks are enabled or disabled during the course of a case instance depending upon a business condition. In Runtime, allocated end users will be able to see the task in their pending lists when the condition is met. If the condition is not met, the task disappears from the Inbox, like it never existed. For more information refer to Conditional activities |
|
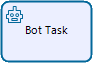
Bot Task |
Is a Task that is performed by an RPA Robot (UiPath or other vendors). For additional information, visite the RPA and robots documentation. |
|
Sub-Process
A Sub-Process is a compound Activity that is included within a Process. Compound means that it can be broken down into lower levels, that is, it contains a set of Activities and a logic sequence (Process) within it.
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
Embedded Sub-Process |
Is an Activity which internal details have been modeled using Activities, Gateways, Events, and Sequence Flows. The shape has a thin border. |
|
Reusable Sub-Process |
Identifies a point in the Process where a predefined Process is used. A Reusable Sub-Process is called a Call Activity in BPMN. The shape has a thick border. |
|
Transactional Sub-Process |
Is a Sub-Process whose behavior is controlled through a transaction protocol. It includes the three basic outcomes of a transaction: Successful Completion, Failed Completion and Cancel Intermediate Event. |
|
Multiple Sub-Process |
Sub-Processes may be repeated sequentially, behaving like a loop. The Multiple Sub-Process iterates a predetermined number of times. The iterations occur sequentially or in parallel (simultaneously). |
|
Gateways
Gateways are used to control the divergence and convergence of sequence flows. They determine ramifications, bifurcations, combinations and merges in the Process. The term “Gateway” implies that there is a gating mechanism that either allows or disallows passage through the Gateway.
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
Exclusive Gateway |
As Divergence: It is used to create alternative paths within the Process, but only one is chosen. As Convergence: It is used to merge alternative paths. |
|
Event Based Gateway |
Represents a branching point in the Process where the alternative paths that follow the Gateway are based on Events that occur. When the first Event is triggered, the path that follows that Event will be used. All the remaining paths will no longer be valid. |
|
Parallel Gateway |
As Divergence: is used to create alternative paths without checking any conditions. As Convergence: is used to merge alternative paths, the gateways waits for all incoming flows before it continues. |
|
Complex Gateway |
As Divergence: is used to control complex decision points in the Process. It creates alternative paths within the Process using expressions. As Convergence: Allows continuation to the next point of the Process when a business condition becomes true. |
|
Inclusive Gateway |
As Divergence: represents a branching point where alternatives are based on conditional expressions. The TRUE evaluation of one condition does not exclude the evaluation of the other conditions. All evaluations of a TRUE condition will be traversed by a token. As Convergence: is used to merge a combination of alternative and parallel paths. |
|
|
A token represents a unit of work that is received by a Process and transferred between different Activities in the Process flow |
Events
An Event is something that happens during the course of the Process, affecting the Process flow and normally has a trigger or result.
To make an Event a throw or a catch Event, right-click it and select Is Throw. This option will enable or disable its behavior (applies for certain Events described below) .
Start Events
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
Start Event |
Indicates where a specific Process starts. It does not have any particular behavior. |
|
Message Start Event |
Is used when a message arrives from a participant and triggers the start of the Process. |
|
Timer Start Event |
Is used when the start of a Process occurs on a specific date or cycle time (e.g., every Friday) |
|
Signal Start Event |
The start of the Process is triggered by the arrival of a signal that has been broadcast from another Process. Note that the signal is not a message; messages have specific targets, signals do not. |
|
Intermediate Events
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
Intermediate Event |
Indicates where something happens somewhere between the start and end of a Process. It will affect the flow of the Process, but will not start or (directly) terminate the Process. |
|
Message Event |
Indicates that a message can be sent or received. If a Process is waiting for a message and it is caught the Process will continue its flow. A catch Message Event waits for a message to arrive and once the message has been received, the Process will continue. The Event marker in this instance will be unfilled. A throw Message Event sends a message to an external participant. The filled Event marker is allocated to the throw message. |
|
Timer Event |
Indicates a delay within the Process. This type of Event can be used within the sequential flow indicating a waiting time between Activities. |
|
Link Event |
This Event is used to connect two sections of the Process. Link Events can be used to create looping situations or to avoid long Sequence Flow lines. If there are two link Events on a Process (one catch and one throw) the Modeler will understand they are linked together. If there is one catch and two throw, the Modeler will understand both throws are received by the catch. If there are several catch and throw Events the name of the 'pairs' must match for the Modeler to understand which throw belongs to which catch. |
|
Signal Event |
These Events are used to send or receive signals within or across the Process. A signal is similar to a signal flare that is shot into the sky for anyone who might be interested to notice and then react. If the Event is used to throw the signal, the signal Event marker will be filled. Alternatively, the unfilled Event marker is allocated to the catch message. |
|
Conditional Event |
These are enabled as soon as a token arrives but will wait until a condition is met to move on to the next step in the process flow. They do not have a user interface and are not disabled, unlike Conditional tasks. For more information refer to Conditional events. |
|
Intermediate Events Attached to an Activity Boundary
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
Compensation Event |
When attached to the boundaries of an activity, this event is used to capture the compensation. When this occurs, the compensation activity will be executed. |
|
Timer Event |
If a Timer Event is attached to the boundary of an Activity, it will change the normal flow into an exception flow when a cycle time is completed or a specific time-date is reached. |
|
Error Event |
A catch Intermediate Error Event can only be attached to the boundary of an Activity.
It reacts to (catches) a named Error, or to any Error if a name is not specified. |
|
Cancel Event |
This Event is used within a Transaction Sub-Process and must be attached to the boundary of one. It shall be triggered if a Cancel End Event is reached within the Transaction Sub-Process. It also shall be triggered if a Transaction Protocol Cancel Message has been received while the transaction is being performed. |
|
End Events
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
End Event |
Indicates when the Process ends. |
|
Message End |
Indicates that a message is sent when the flow has ended. |
|
Error End |
Indicates that a named Error should be generated. All currently active threads of the Process are terminated. The Error will be caught by a Catch Error Intermediate Event. |
|
Cancel End |
Is used within a Transaction Sub-Process. It indicates that the Transaction should be canceled and an alternative flow can be performed. |
|
Signal End |
Indicates that a signal is sent when the flow has ended. |
|
Terminate End |
Ends the Process and all its Activities immediately. |
|
Artifacts
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
Group |
Is an Artifact that provides a visual mechanism to group elements of a diagram informally. |
|
Annotation |
Is a mechanism for a modeler to provide additional information for the reader of a BPMN Diagram. |
|
Data Objects |
Provides information about how documents, data and other objects are used and updated during the Process. |
|
Swim lanes
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
Pool |
A Pool is a container of a single Process (contains the sequence flows between Activities). A Process is fully contained within the Pool. There is always at least one Pool. |
|
Lane |
Is a sub-partition within the Process. Lanes are used to differentiate elements as internal roles, position, department, etc. They represent functional areas that may be responsible for tasks. |
|
Milestone |
Is a sub-partition within the Process. It can indicate different stages during the Process. |
|
Connectors
ELEMENT |
DESCRIPTION |
NOTATION |
|---|---|---|
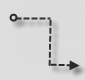
Sequence Flow |
A Sequence Flow is used to show the order that Activities will be performed in the Process. |
|
Association |
Its used to associate information and Artifacts with Flow Objects. It also shows the Activities used to compensate for an Activity. |
|
Message Flow |
Is used to show the flow of messages between two entities that are prepared to send and receive them. |
|
You can find more information about modeling for automation in our Bizagi Modeler Help documentation.
Download our BPMN 2.0 Poster
Last Updated 2/27/2024 4:03:08 PM